What Is The Potential Difference Across The 10 ω Resistor - According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). The potential difference across the. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v.
The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across the. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r.
In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). The potential difference across the.
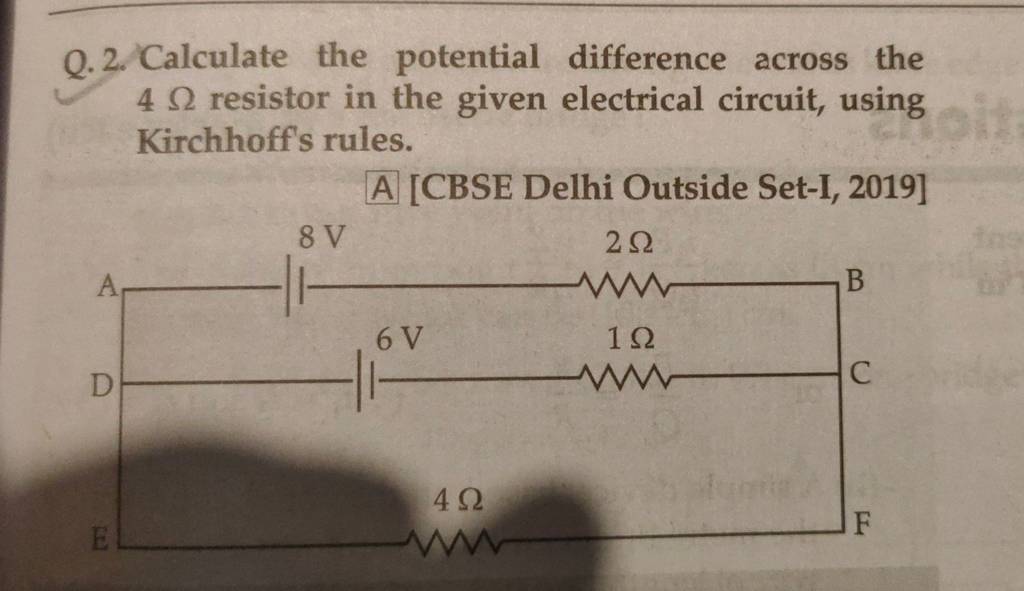
Q.2. Calculate the potential difference across the 4Ω resistor in the giv..
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v..
The potential difference across resistor R3 is Filo
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. The potential difference across the. In theory, for a current of 2a, the.
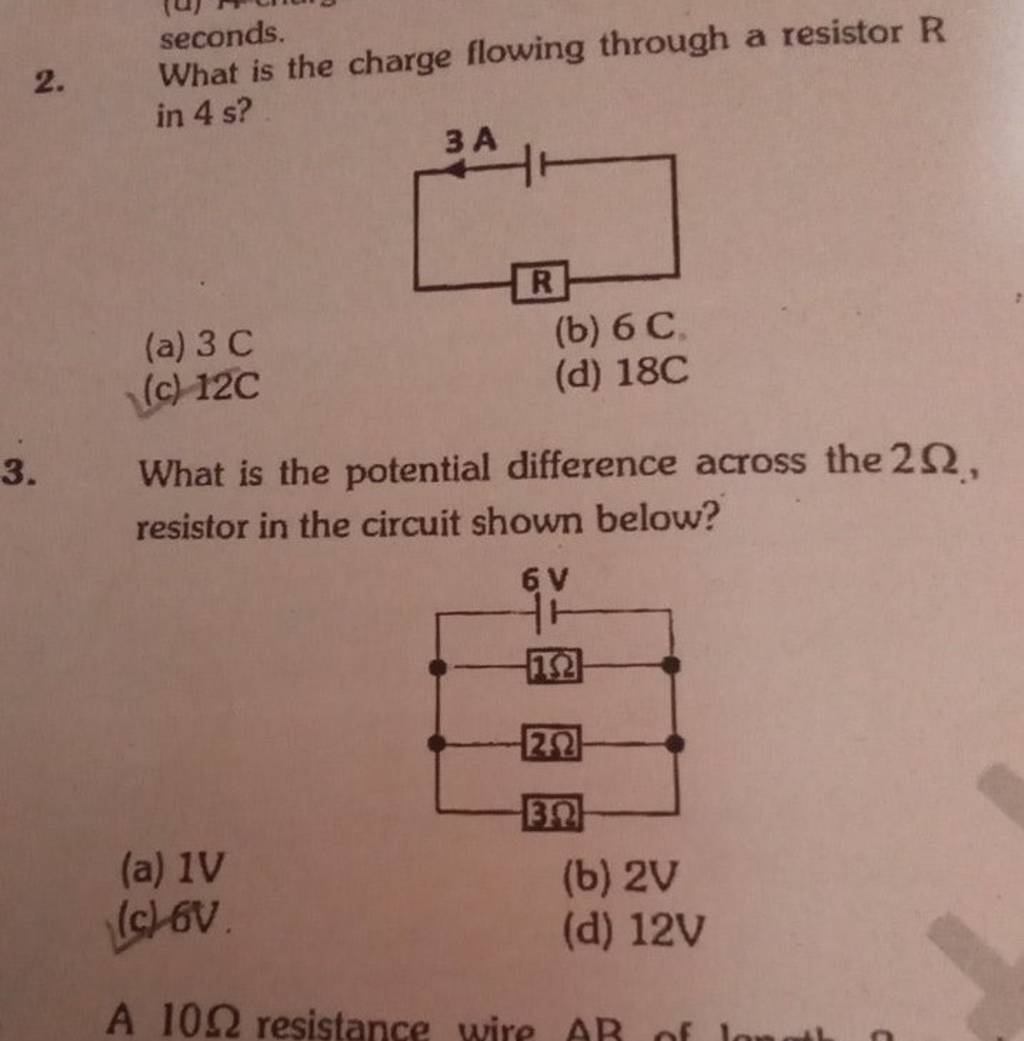
What is the potential difference across the 2Ω, resistor in the circuit s..
The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference across.
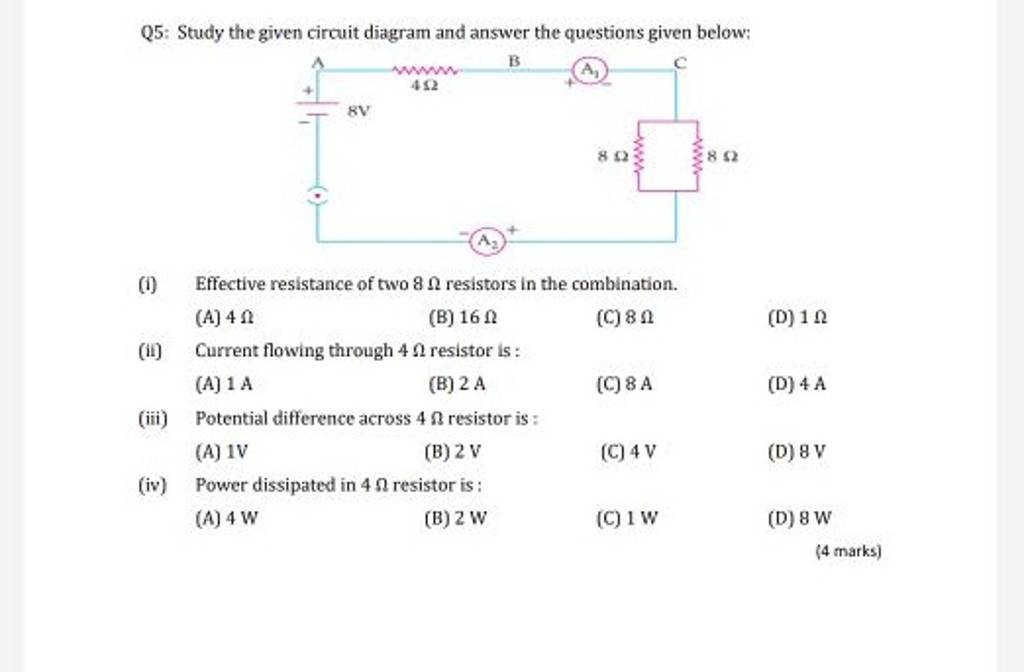
Potential difference across 4Ω resistor is Filo
The potential difference across the. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to.
Solved Part A What is the potential difference across the
The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). The potential difference across the. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω.
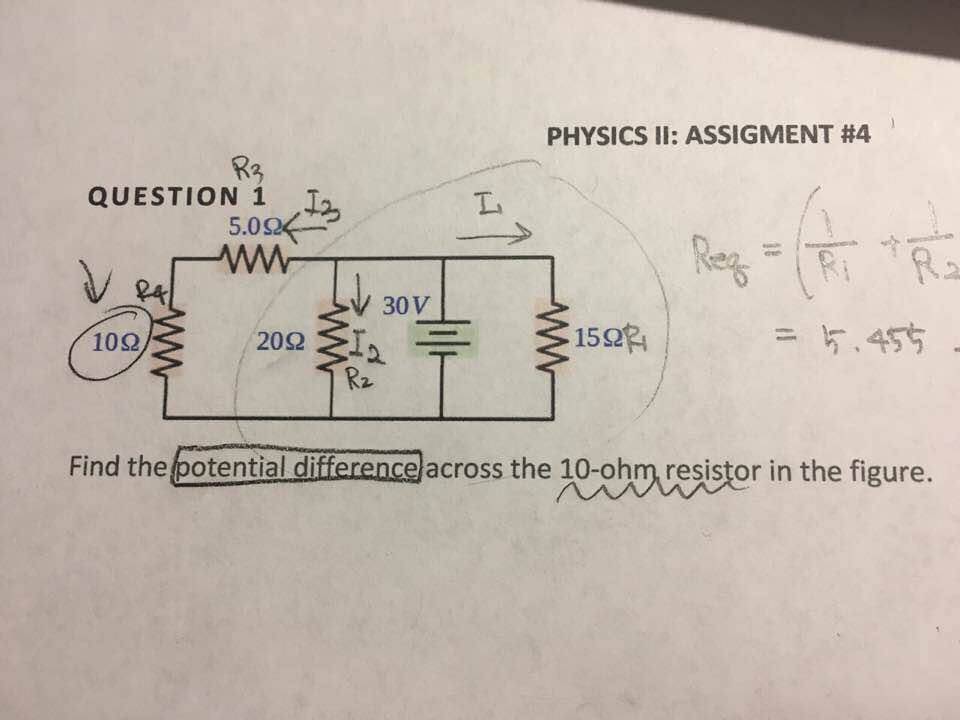
Solved Find the potential difference across the 10ohm
In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. The potential difference across the. According to ohm’s.
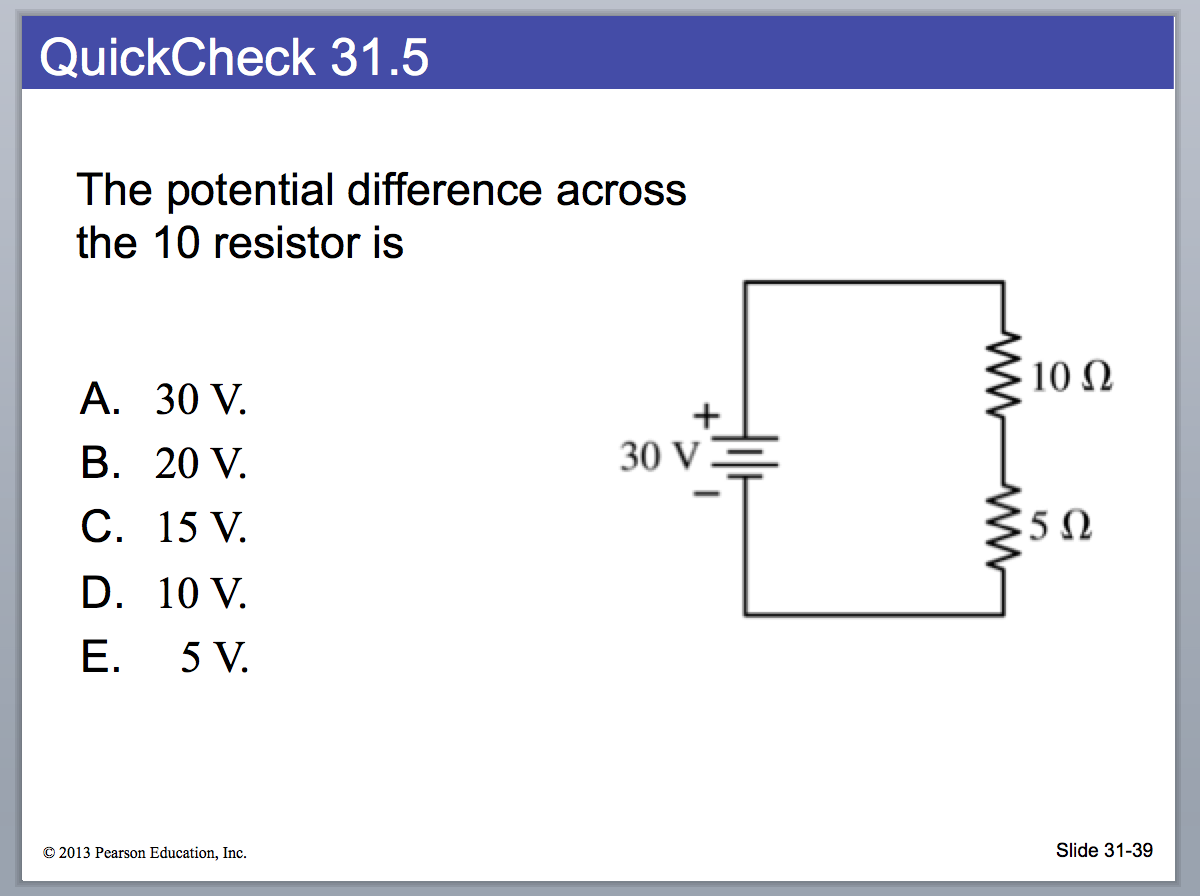
Solved The potential difference across the 10 resistor is A.
The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across.
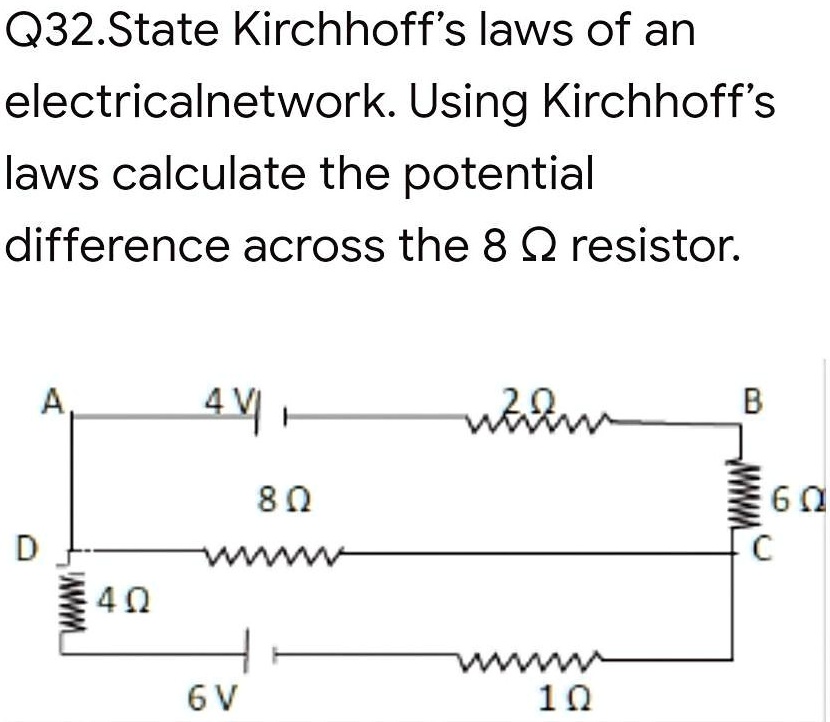
Find potential difference through an 8ohm resistor. Q32. State
The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference across the. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω.
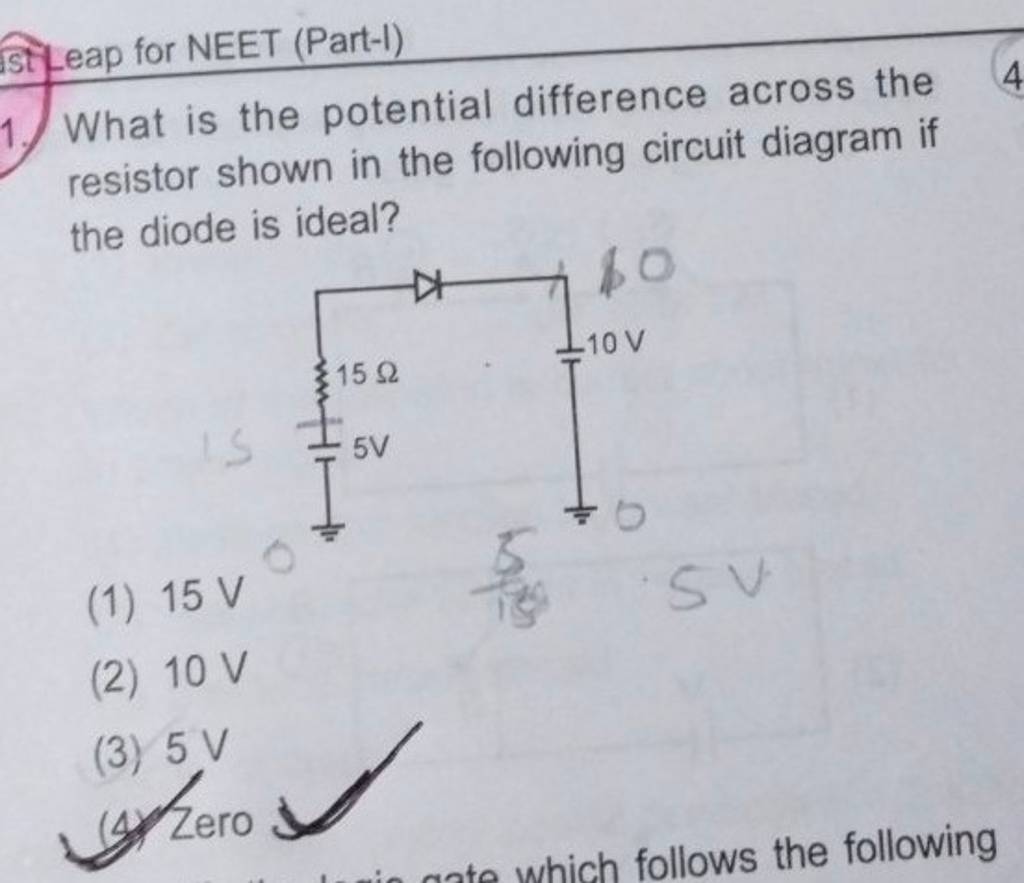
What is the potential difference across the resistor shown in the followi..
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω + 5 ω) = (2 a) (10 ω + 5 ω) = 30 v. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across.
potential difference V across the resiven resistor for the corresponding
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. The potential difference across the. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r). The potential difference in the upper branch could be calculated by v = i (10 ω.
The Potential Difference In The Upper Branch Could Be Calculated By V = I (10 Ω + 5 Ω) = (2 A) (10 Ω + 5 Ω) = 30 V.
The potential difference across the. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. In theory, for a current of 2a, the potential. The potential difference across a resistor can be found using ohm's law (v=i*r).