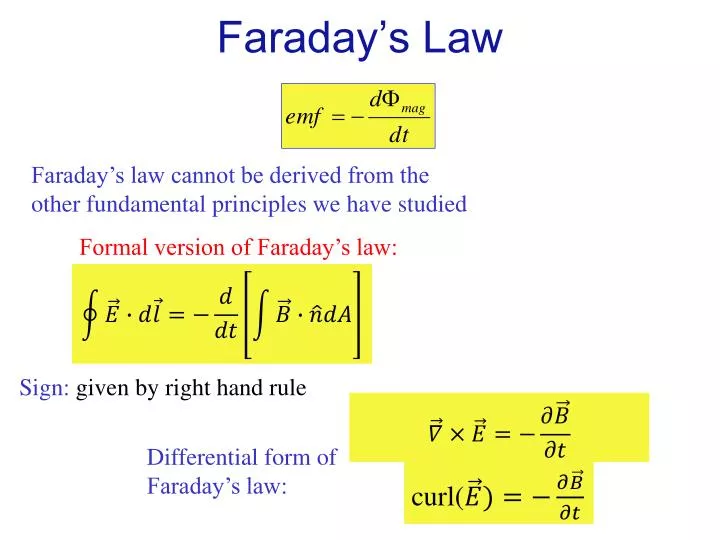
Faraday S Law Integral Form - Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of.
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in.
Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of.
SOLUTION Integral and differential forms of faraday s law Studypool
Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd.
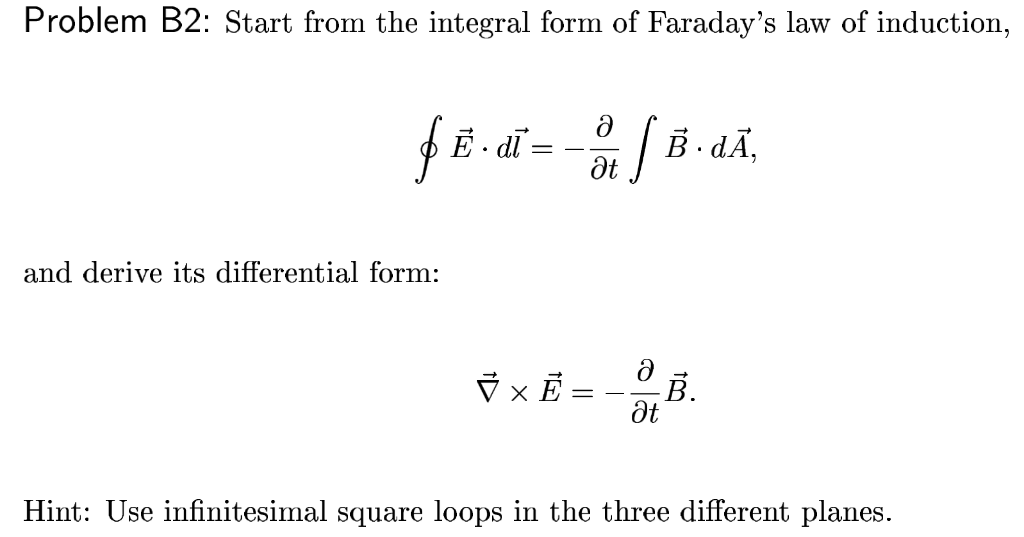
Solved Problem B2 Start from the integral form of Faraday's
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s.
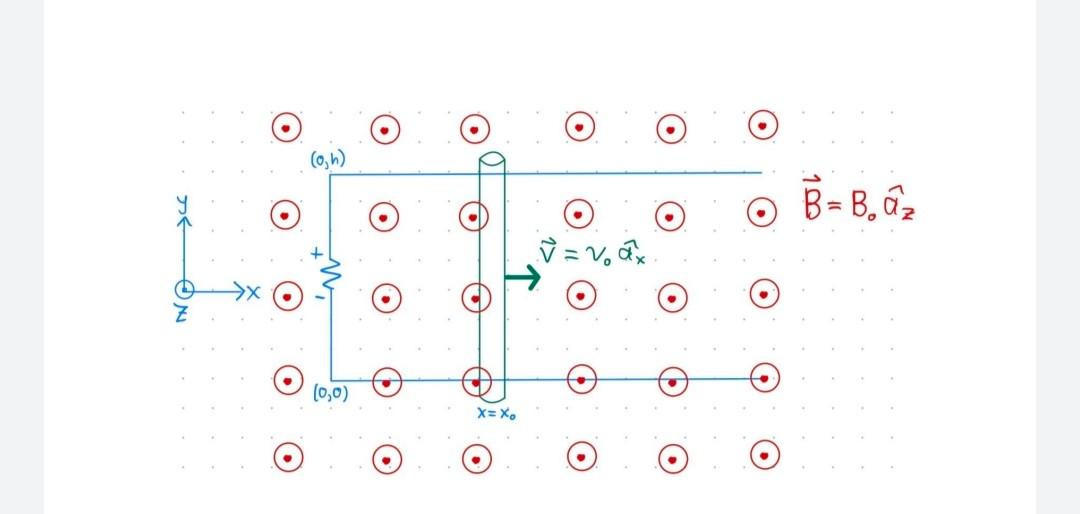
Solved Problem 9 (5 points) Faraday's Law (Integral Form)
Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s.
(PDF) Path Integral Approach to Faraday's Law of Induction
Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd.
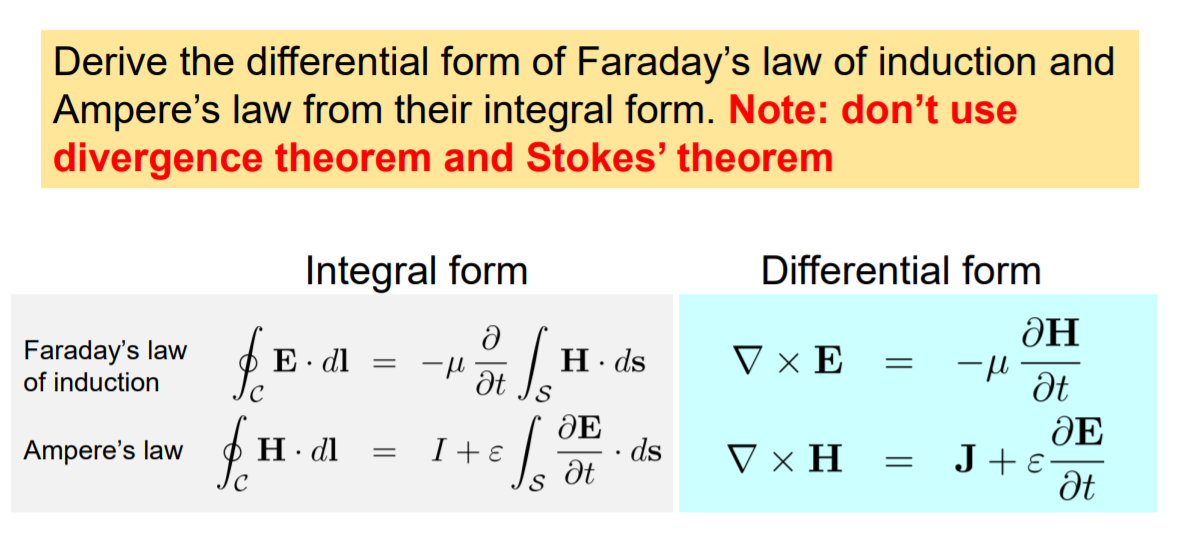
Solved Derive the differential form of Faraday's law of
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the.
Faraday's Law Understanding the Alternative (Integral Form)
Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s.
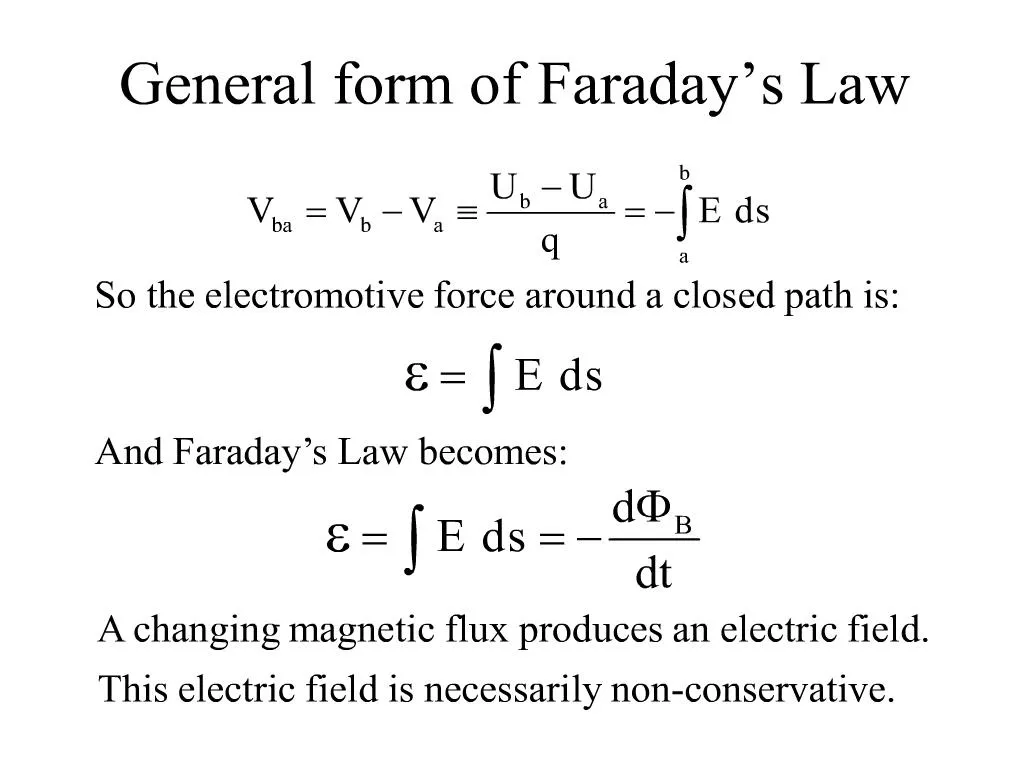
PPT general form of faraday s law PowerPoint Presentation, free
Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s.
Solved Faraday's Law can be written in integral form as
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the.
PPT Faraday’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3607741
Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd maxwell equation): Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s.
SOLUTION Integral and differential forms of faraday s law Studypool
Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in. Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Let's consider both the integral and differential equations which express the faraday law (3rd.
Let's Consider Both The Integral And Differential Equations Which Express The Faraday Law (3Rd Maxwell Equation):
Therefore, faraday’s law (2.1) becomes s (r e) ds = d dt s bds = s @b @t ds (2.9) where we have exchanged the order of. Faraday’s law outline •faraday’s experiment •two ways to calculate induced emf •faraday’s law in integral form •faraday’s law in.