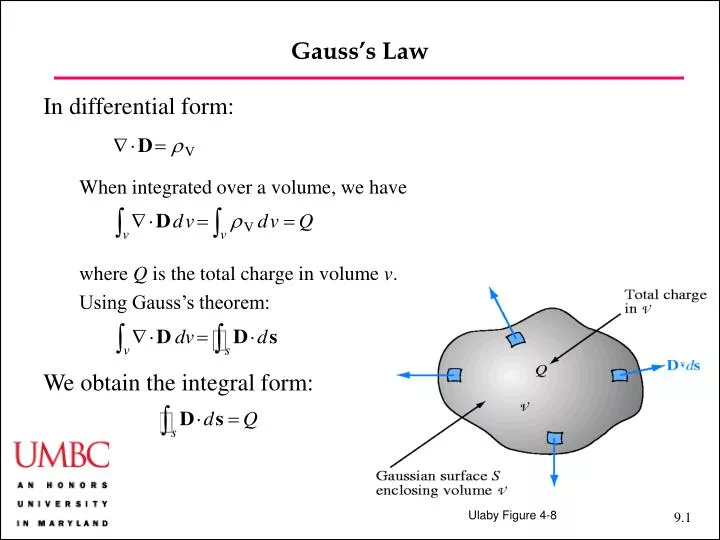
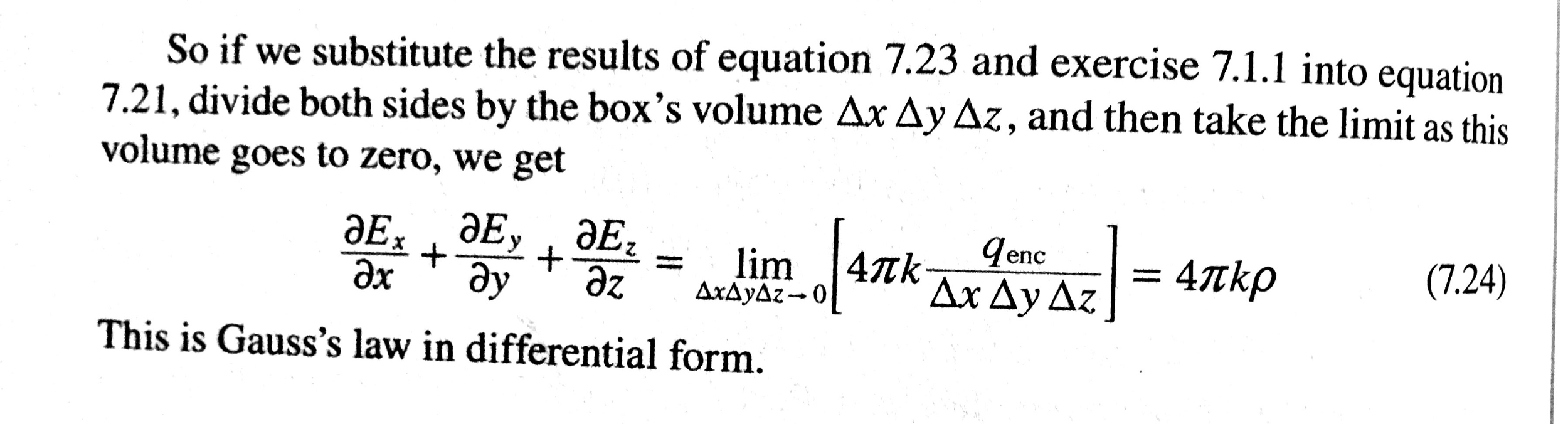Gauss S Law Differential Form - The divergence of electric field at each point is proportional to the local charge. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: 13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. The divergence of a coulomb field; 14 conservative fields and energy. The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states:
Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. 13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. The divergence of a coulomb field; Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. 14 conservative fields and energy. The divergence of electric field at each point is proportional to the local charge. The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states:
14 conservative fields and energy. The divergence of a coulomb field; It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states: This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. 13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: The divergence of electric field at each point is proportional to the local charge.
Differential Integral Form Gauss Law Stock Vector (Royalty
This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. The divergence of a coulomb field; Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. 14 conservative fields and energy. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law:
electrostatics Problem in understanding Differential form of Gauss's
14 conservative fields and energy. The divergence of a coulomb field; 13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: The divergence of electric field at each point is proportional to the local charge.
Solved BOX 7.1 Gauss's Law in Integral and Differential Form
Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. 14 conservative fields and energy. The divergence of a coulomb field;
Gauss's Law Formula Equation Calculation
The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states: 14 conservative fields and energy. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,.
Solved Using the differential form of Gauss's law, determine
13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states:
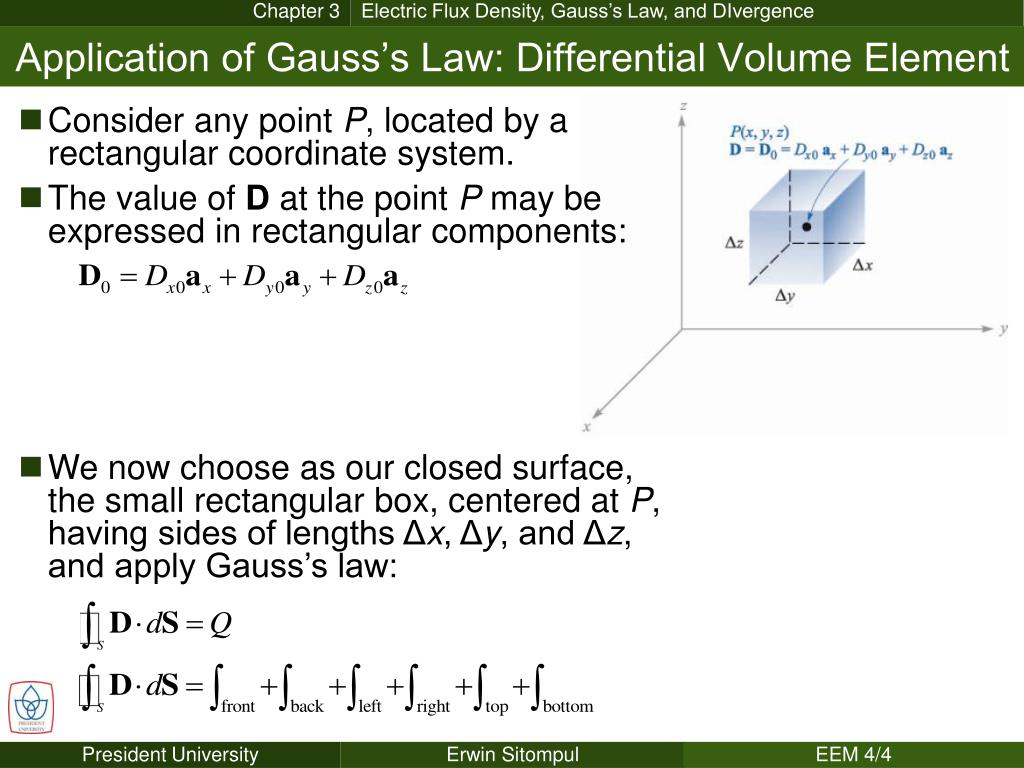
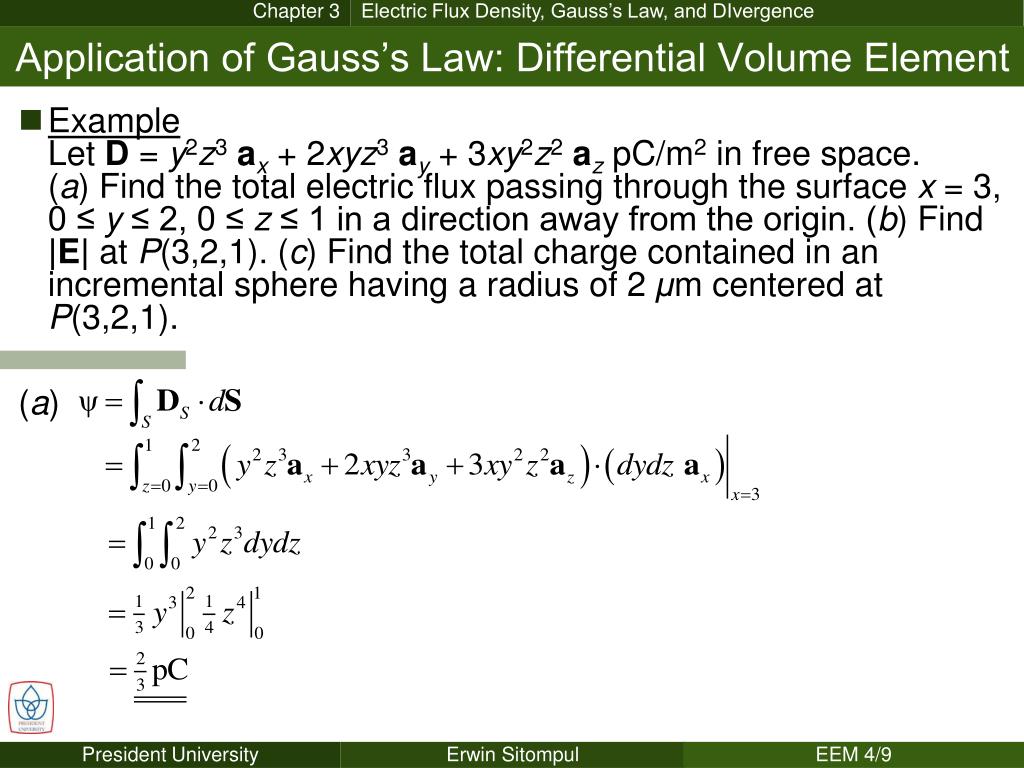
PPT Application of Gauss’s Law Differential Volume Element
Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. The divergence of a coulomb field; Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. 14 conservative fields and energy.
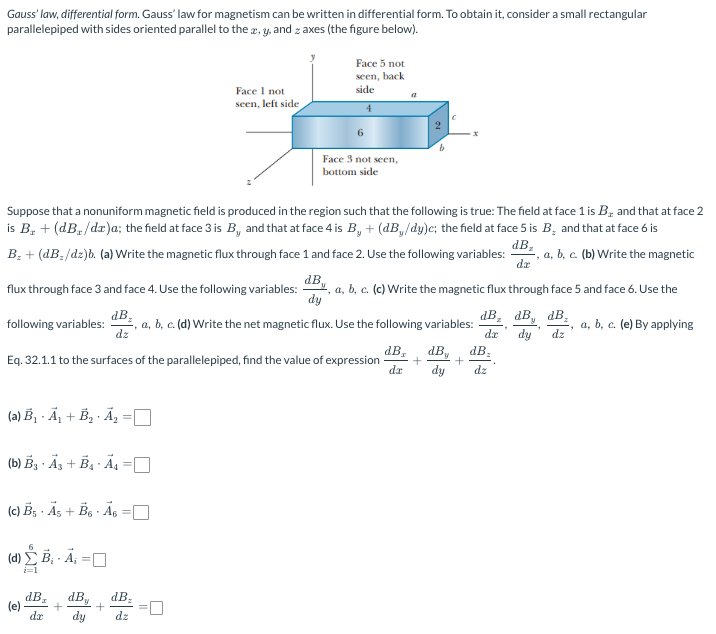
Solved Gauss' law, differential form. Gauss' law for
The divergence of electric field at each point is proportional to the local charge. The divergence of a coulomb field; 14 conservative fields and energy. This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law:
SOLUTION Integral and differential form of gauss s law Studypool
13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. It states that the divergence of the electric field at any. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law:
PPT Application of Gauss’s Law Differential Volume Element
The divergence of a coulomb field; The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states: This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. It states that the divergence of the electric field at.
Gauss Law
The divergence of a coulomb field; The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states: This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: = where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,.
It States That The Divergence Of The Electric Field At Any.
The divergence of a coulomb field; This conclusion is the differential form of gauss' law, and is one of maxwell's equations. 14 conservative fields and energy. The differential form of gauss's law, involving free charge only, states:
The Divergence Of Electric Field At Each Point Is Proportional To The Local Charge.
= where ∇ · d is the divergence of the electric displacement field,. Gauss’ law in differential form (equation \ref{m0045_egldf}) says that the electric flux per unit volume originating from a. 13 gauss's law (differential form) differential form of gauss' law; Differential form (“small picture”) of gauss’s law: