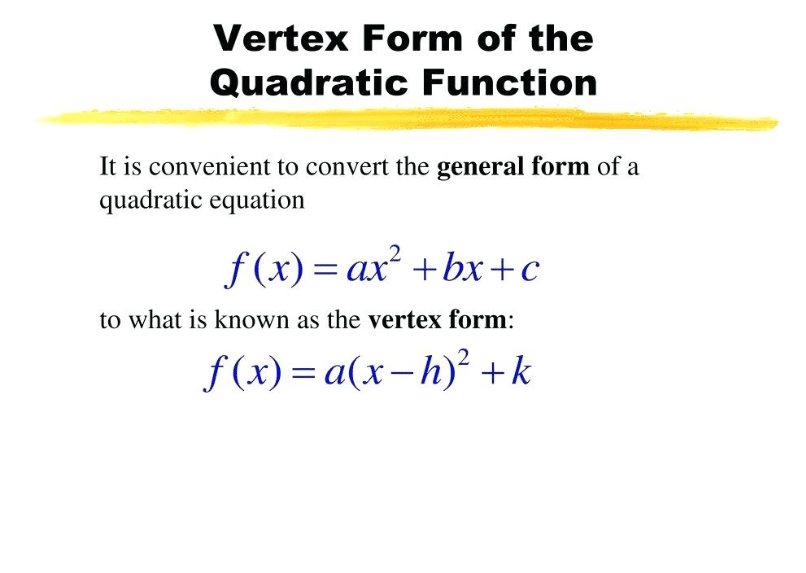
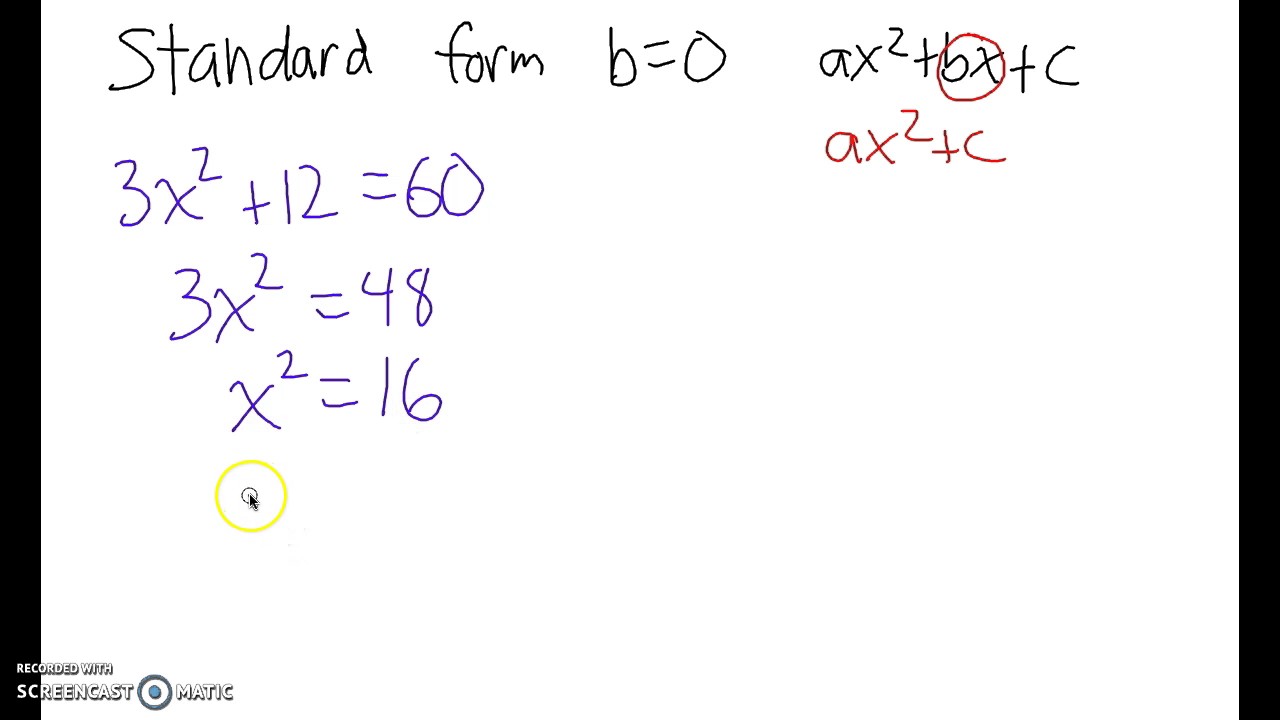How To Find The Standard Form Of A Quadratic Equation - In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Standard form of quadratic equation is:
In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: The standard form of a quadratic equation is:
In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0.
Standard Form Of Quadratic Equation 2 Things To Expect When Attending
The standard form of a quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: Ax2 + bx + c = 0.
Standard Form of Quadratic Equation with Examples
The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and.
Different Forms of Quadratic Equation with Examples
Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is:
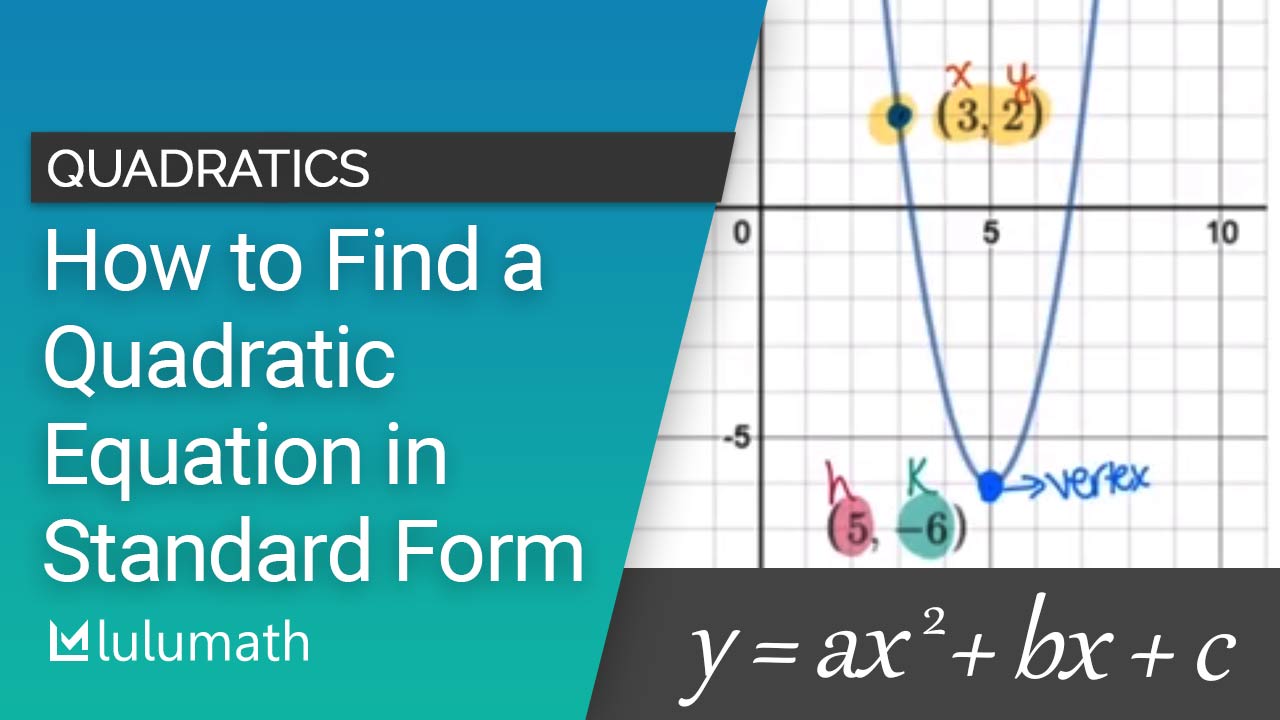
Finding Quadratic Equation in Standard Form (VIDEO) Lulumath
In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax2 + bx + c = 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is:
Quadratic Equation Graph Standard Form Examples
Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and.
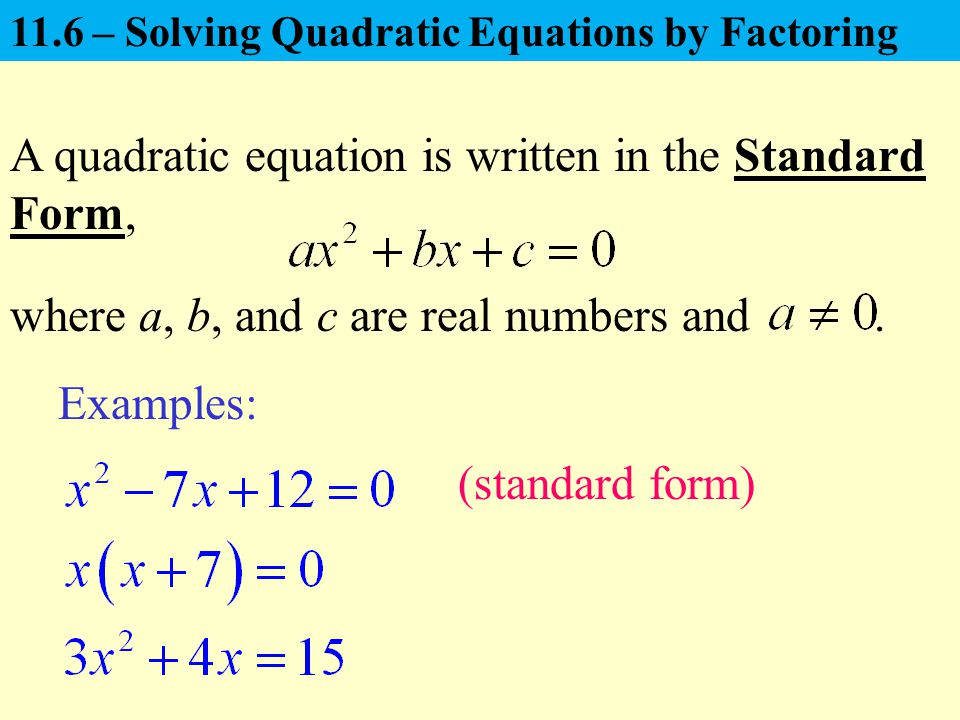
Quadratic Equation Examples Standard Form Tessshebaylo
Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: Ax2 + bx + c = 0. In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. The standard form of a quadratic equation is:
40 Standard Form Quadratic Equation Images, Stock Photos & Vectors
The standard form of a quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Standard form of quadratic equation is: Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0.
Quadratic Equation Graph Standard Form Examples
Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and.
Different Forms of Quadratic Equation with Examples
Ax2 + bx + c = 0. The standard form of a quadratic equation is: In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. Standard form of quadratic equation is:
Ax2 + Bx + C = 0.
The standard form of a quadratic equation is: Ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0. In the equation, a, b, and c are constants, and. Standard form of quadratic equation is: