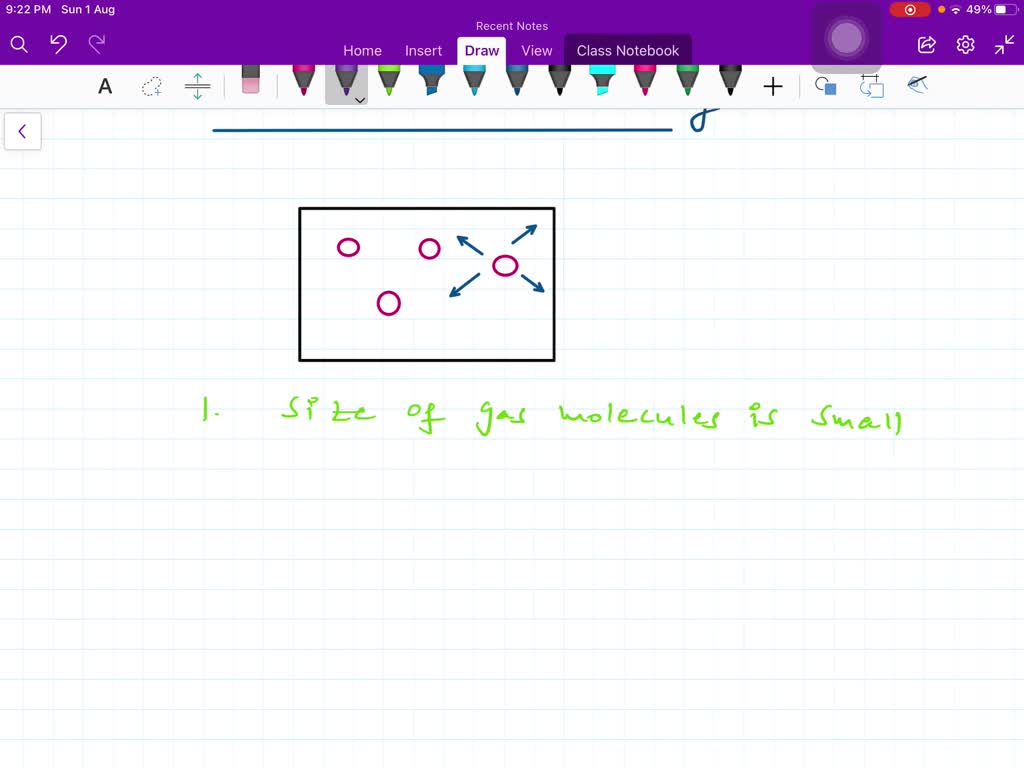
What Are The Five Basic Postulates Of Kinetic Molecular Theory - The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume.
The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas.
The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas.
Molecular Theory Cuestionario
The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described.
SOLUTION Molecular Theory And its Postulates Studypool
The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated.
The Molecular Theory PPT
The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior.
SOLVEDState the five postulates of the theory.
The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior.
SOLVEDList the five basic postulates of the theory
The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws.
⇉3 Postulates Of The Molecular Theory Essay Example GraduateWay
The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules.
SOLUTION Basic postulates of molecular theory Studypool
The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described.
2 Molecular Theory PDF Gases Temperature
The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study.
molecular theory 10.1 PPT
The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws.
Molecular Theory PDF Gases Energy
The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume. The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is directly proportional to the kelvin temperature of the gas (charles' law) study with quizlet and. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws.
The Average Kinetic Energy Of The Gas Particles Is Directly Proportional To The Kelvin Temperature Of The Gas (Charles' Law) Study With Quizlet And.
The kinetic molecular theory of gases begins with five postulates that describe the behavior of molecules in a gas. The kinetic molecular theory (kmt) is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this. The first postulate (or assumption) states that gases consist of particles that are treated as if they have no volume.