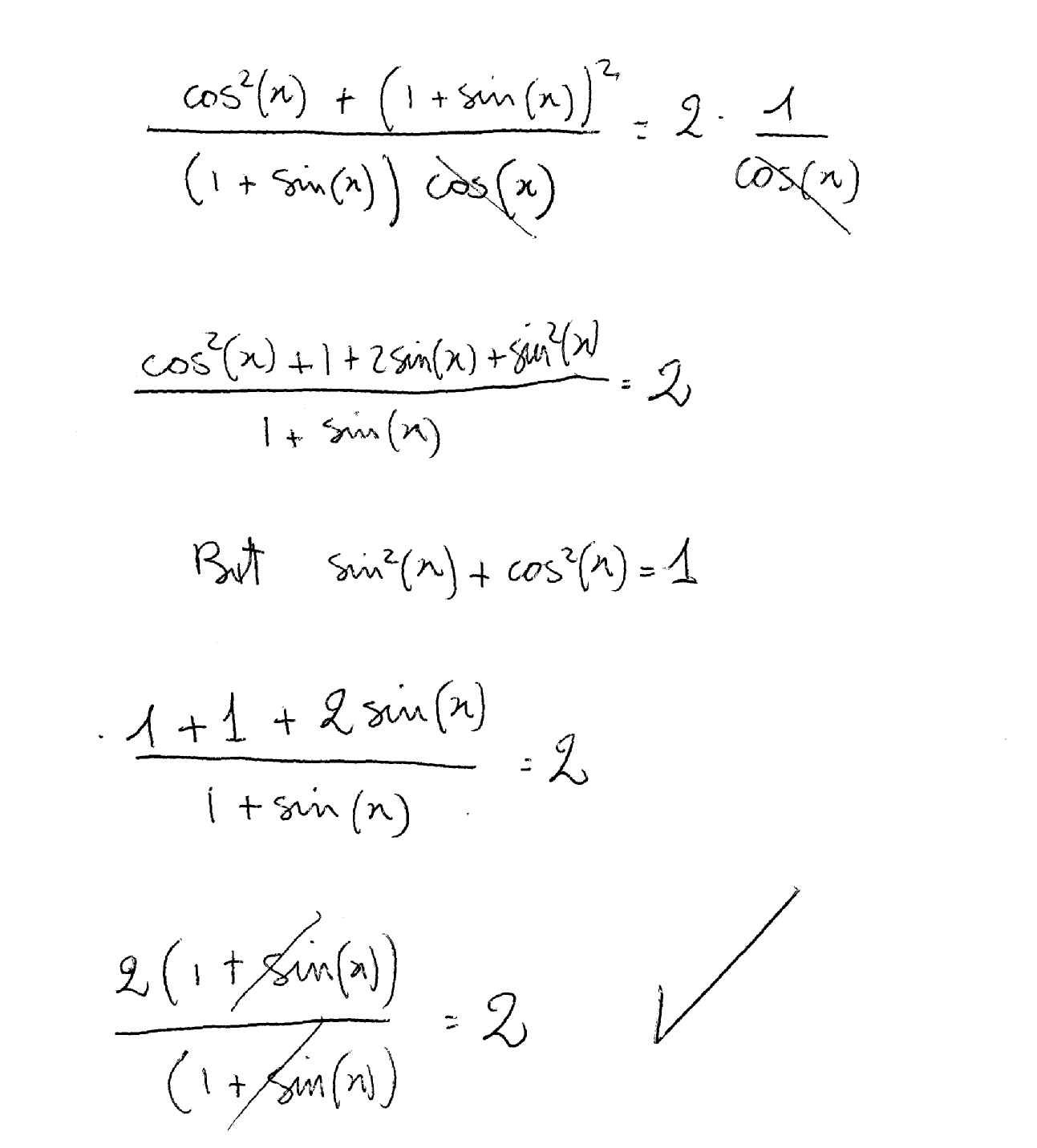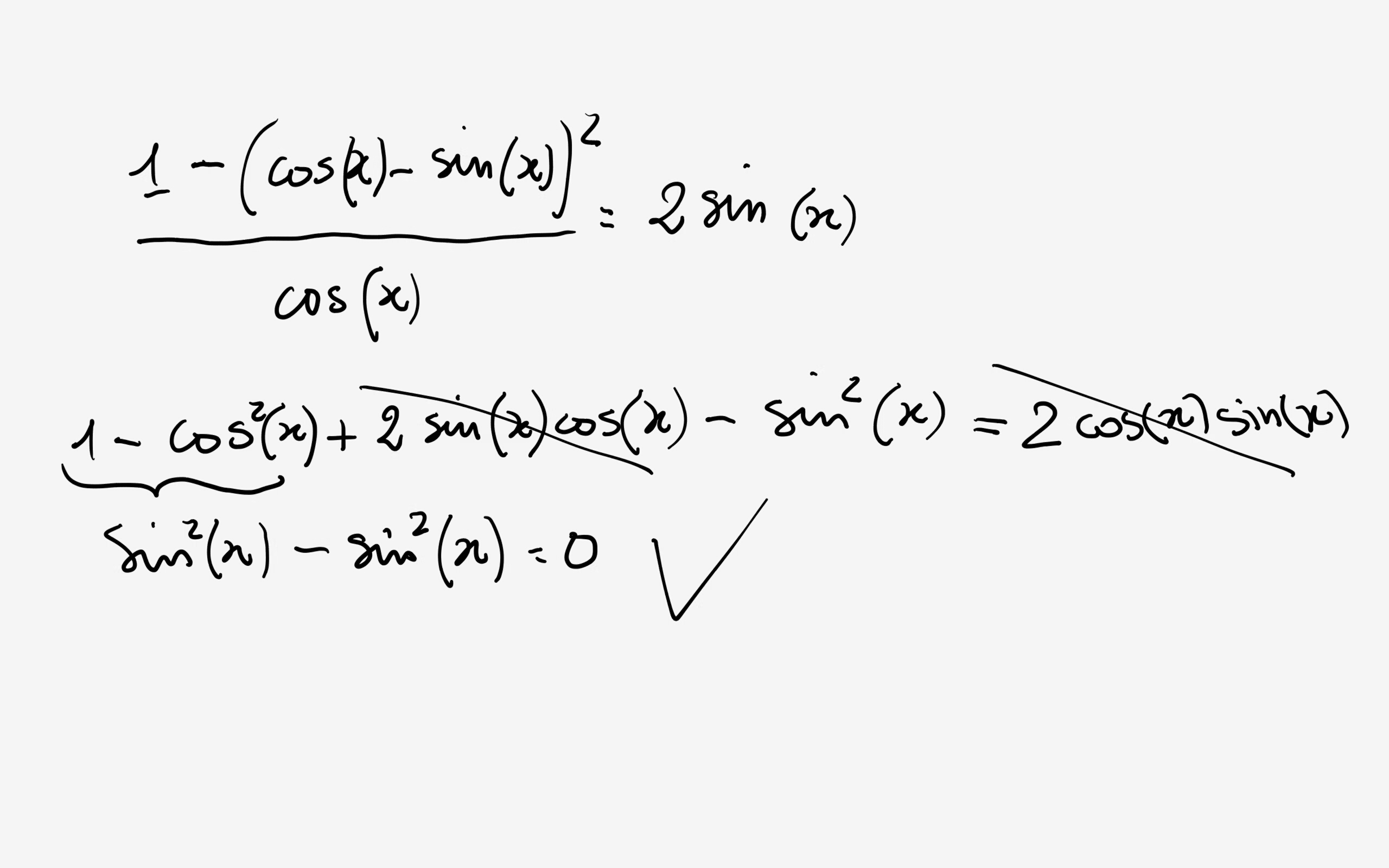What Is Cosx Sinx - Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse.
Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent.
Given Sinx 0.3 What Is Cosx
Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1.
Graph of sin(x) and cos(x) Download Scientific Diagram
Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse.
How do you verify this identity (cosx)/(1+sinx) + (1+sinx)/(cosx
Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse.
Given Sinx 0.9 What Is Cosx
Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1.
(sinx)^2+(cosx)^2=1 Physics and mathematics, Mathematics, Math
Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse.
Prove that, (1+sinxcosx)/(1+sinx+cosx)+(1+sinx+cosx)/(1+sinxcosx
Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Trigonometric Identity (1 Cosx)/sinx Sinx/(1 Cosx) 2/sinx, 43 OFF
Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Given Sinx 0.3 What Is Cosx
Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.
Find the derivatives of sinx cosx Yawin
Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse.
trigonometry Transformation of \cos(x) to \sin(x) via \cos(x+
Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse. Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Tan (θ) = opposite / adjacent. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1.
Tan (Θ) = Opposite / Adjacent.
Sin (θ) = opposite / hypotenuse. Compute answers using wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. Cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2(cosx)2 1. Cos (θ) = adjacent / hypotenuse.