What Is Squamous Mucosa With Reactive Epithelial Changes - Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal. It may be a noncancerous or. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. The lining of the esophagus is known as the “mucosa.” most of the esophagus is lined by squamous cells,.
Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? The lining of the esophagus is known as the “mucosa.” most of the esophagus is lined by squamous cells,. Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. It may be a noncancerous or. Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal.
Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. It may be a noncancerous or. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. The lining of the esophagus is known as the “mucosa.” most of the esophagus is lined by squamous cells,. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal.
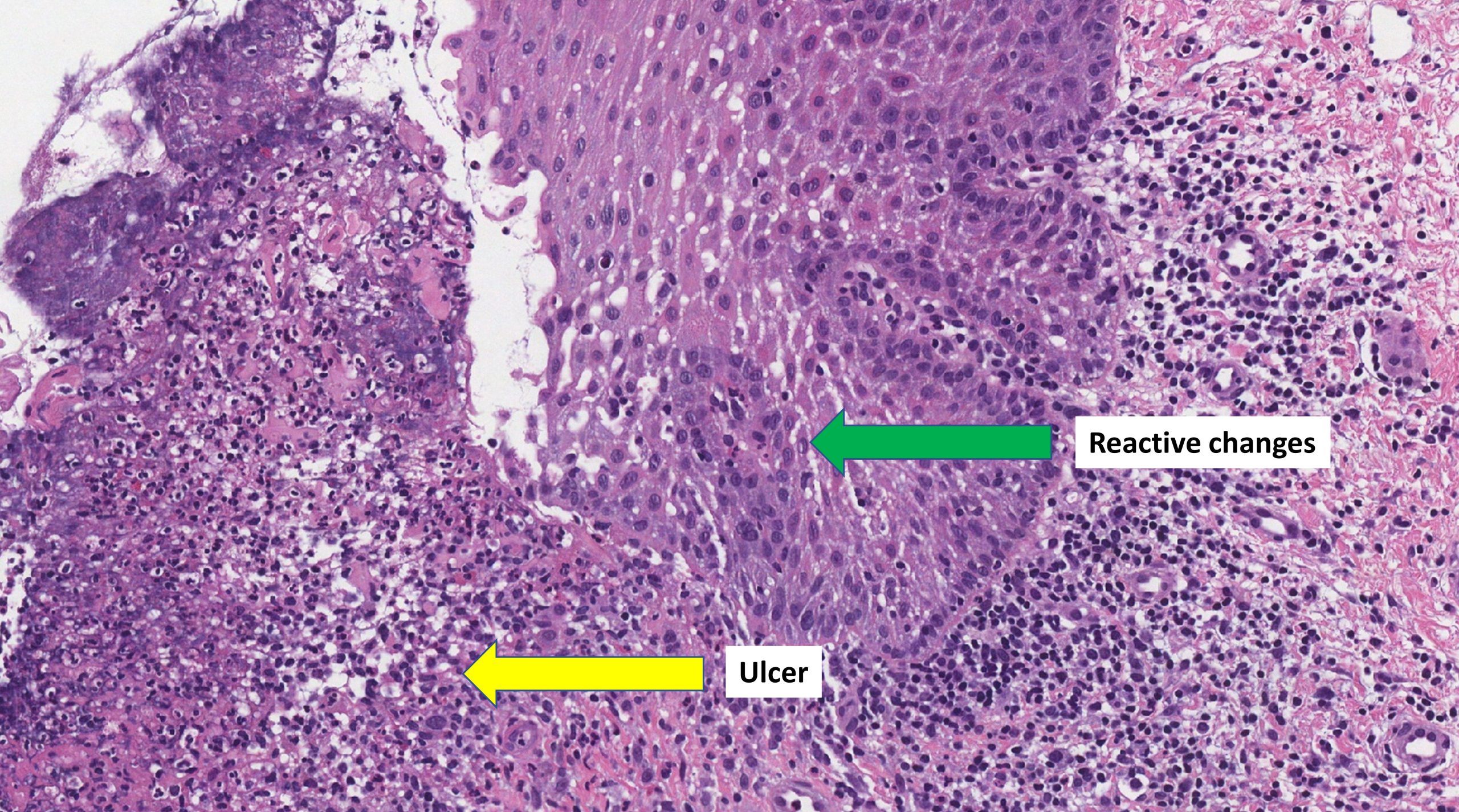
Reactive changes MyPathologyReport.ca
Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? The lining of the esophagus is known as the “mucosa.” most of the esophagus is lined by squamous cells,. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous.
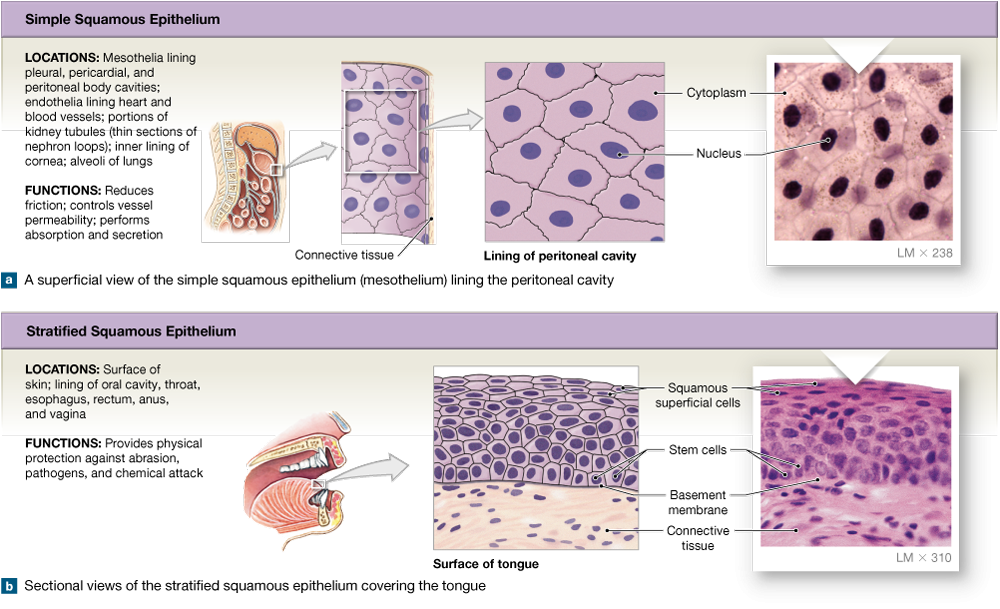
Squamous epithelium
Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found..
Squamous epithelium MyPathologyReport.ca
Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue.
Squamous Mucosa edu.svet.gob.gt
Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. It may be a noncancerous or.
− Benign reactive cellular changes associated with radiation A
Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. It may be a noncancerous or. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue.
Biopsy showing (A) squamous mucosa with acute inflammation and reactive
When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Squamous mucosa in the esophagus refers to the thin, flat epithelial cells lining the esophagus, playing a key role in protection and. The lining of the esophagus is known as the “mucosa.” most of the esophagus is lined by squamous cells,. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia..
NonKeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Of The Human Esophagous
It may be a noncancerous or. When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. What does “squamous mucosa” mean?
Biopsy showing (A) squamous mucosa with acute inflammation and reactive
Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal. It may be a noncancerous or. What does “squamous mucosa” mean? Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia.
Overlying squamous mucosa in case 2 showing marked... Download
What does “squamous mucosa” mean? When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. The lining of the esophagus is known as the “mucosa.” most of the esophagus is lined by squamous cells,. Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa.
Simple Squamous Epithelium Function Quizlet Slide Share Anatomy
It may be a noncancerous or. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous. Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia. What does “squamous mucosa” mean?
Squamous Mucosa In The Esophagus Refers To The Thin, Flat Epithelial Cells Lining The Esophagus, Playing A Key Role In Protection And.
Squamous mucosa is a thin layer of tissue that covers the inside surface of the mouth, esophagus, vagina, cervix, and anal canal. It may be a noncancerous or. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place squamous mucosa is normally found. When intestinal metaplasia replaces the squamous.
The Lining Of The Esophagus Is Known As The “Mucosa.” Most Of The Esophagus Is Lined By Squamous Cells,.
What does “squamous mucosa” mean? Changes to epithelial cells that line organs, glands and skin cause squamous metaplasia.