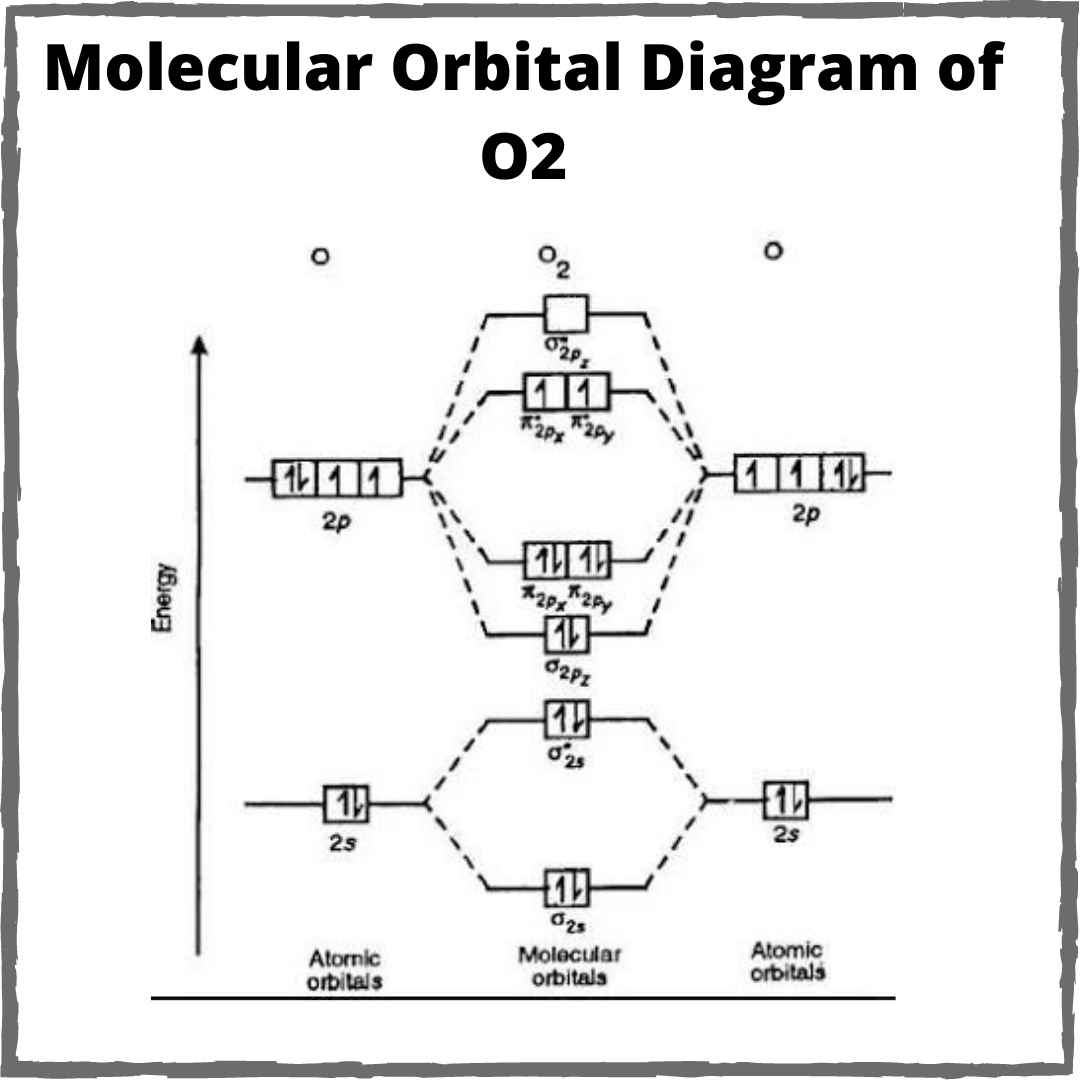
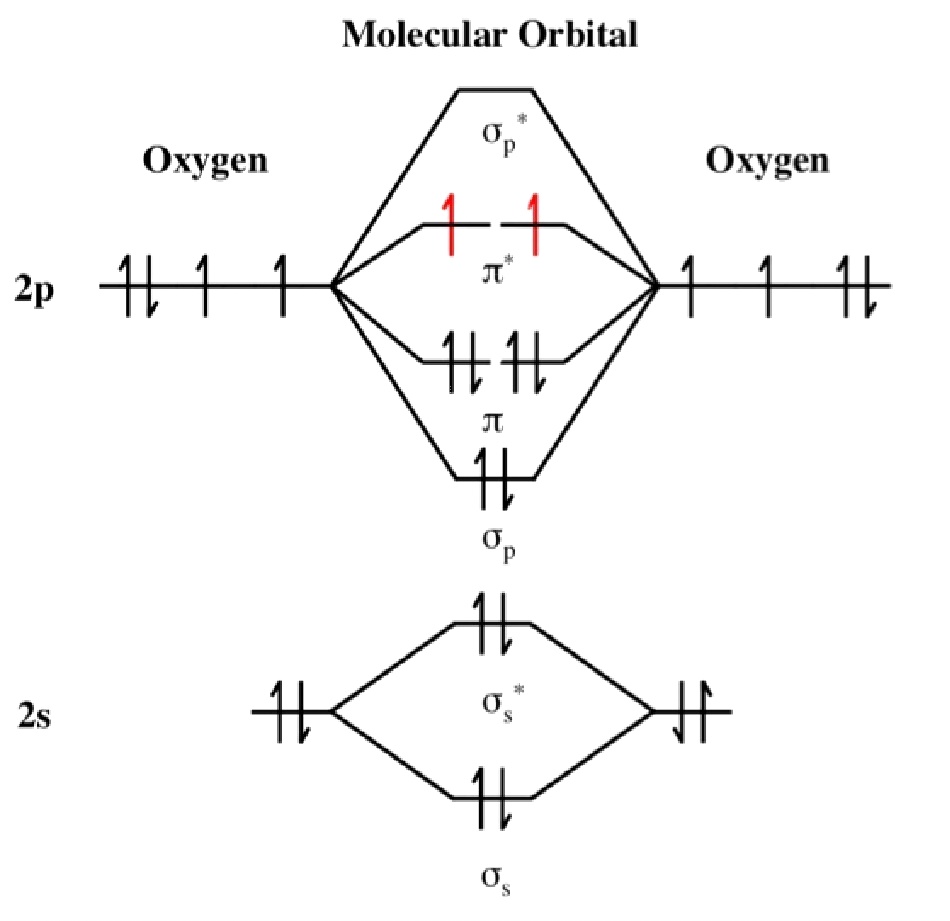
What Is The Bond Order Of O2 - What is the bond order in o2 +? O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. The bond order of o2 is 1. Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. Bond order is associated with the strength of bond and bond length. The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length. O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. O 2 has 16 electrons. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2).
What is the bond order in o2 +? O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2). The bond order of o2 is 1. Bond order is associated with the strength of bond and bond length. Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. O 2 has 16 electrons. A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron.
Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. What is the bond order in o2 +? The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2). A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. The bond order of o2 is 1. O 2 has 16 electrons. Remember that the bond order is the number of bonds between two atoms. The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length.
Bond Order Of N2 astonishingceiyrs
O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. The bond order of o2 is 1. Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons.
O2 Bond Order Diagram
O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. Remember that the bond order is the number of bonds between two atoms. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has.
MO DIAGRAM of O2,O2,O2+ THEIR BOND ORDER AND CHAR
The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length. A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. The bond order of o2 is 1. Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons.
O2 Bond Order Diagram
What is the bond order in o2 +? The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2). A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. O2 has a bond order of 2 and.
Calculate the bond order of N2,O2,O2^+and O2^ Chemistry Chemical
What is the bond order in o2 +? Bond order is associated with the strength of bond and bond length. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2). O2 has a bond.
What is meant by term bond order? Write bond orders for N2, O2?
O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2). What is the bond order in o2 +? O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. The.
Understanding the Bond Order in O2 through Molecular Orbital Diagrams
The bond order of o2 is 1. O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. Bond order is associated with the strength of bond and bond length. The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length.
Explain why the bond order of N2 is greater than N2+, but the bond
A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. The bond order of o2 is 1. What is the bond order in o2 +? The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length.
The bond order of O_2^+ is the same as in
O 2 has 16 electrons. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length. O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of.
Calculate the bond order in O_2,O_2^,O_2^{2} and O_2^+ molecule.
Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. O 2+ loses one electron, leaving 15 electrons. The bond order of o2+ is 2.5, indicating that it has a stable bond that is stronger than that of o2 (which has a bond order of 2). O2 has a bond order of 2 and two unpaired electrons in its π* orbitals. The higher the.
The Bond Order Of O2+ Is 2.5, Indicating That It Has A Stable Bond That Is Stronger Than That Of O2 (Which Has A Bond Order Of 2).
The bond order of o2 is 1. Remember that the bond order is the number of bonds between two atoms. Bond order is associated with the strength of bond and bond length. O 2 has 16 electrons.
O2 Has A Bond Order Of 2 And Two Unpaired Electrons In Its Π* Orbitals.
A bond order of 1 indicates a stable molecule, as there is one net bonding electron. What is the bond order in o2 +? Over o2⁻, o2⁺ is more stable. The higher the bond order, the smaller will be the bond length.