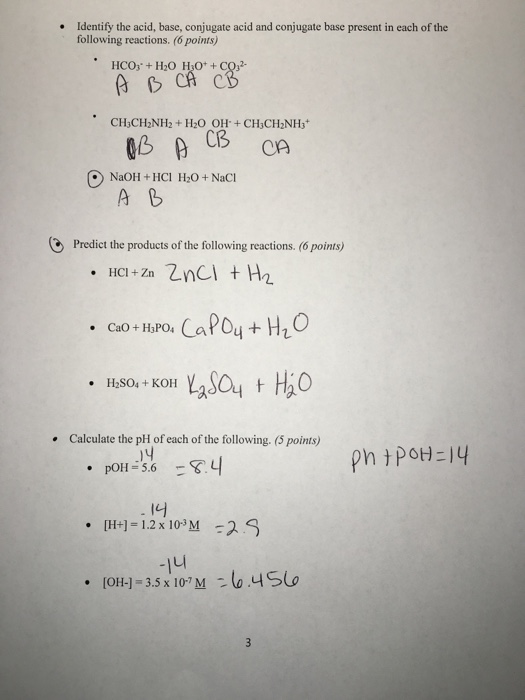What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Ch3Nh2 - The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming.
The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming.
For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺.
Solved 1 Acids and Conjugate Bases Identify the conjugate
The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺.
SOLVED 8. Identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base
When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction:
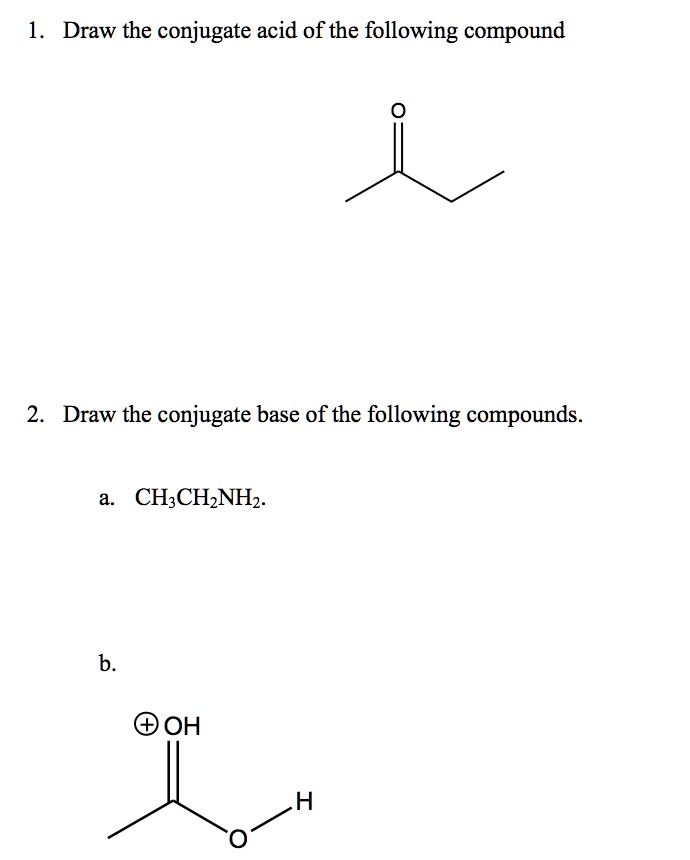
SOLVED Draw the conjugate acid of the following compound CH3CH2NH2
Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺.
Answered 5. For each reaction, identify the… bartleby
When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+.
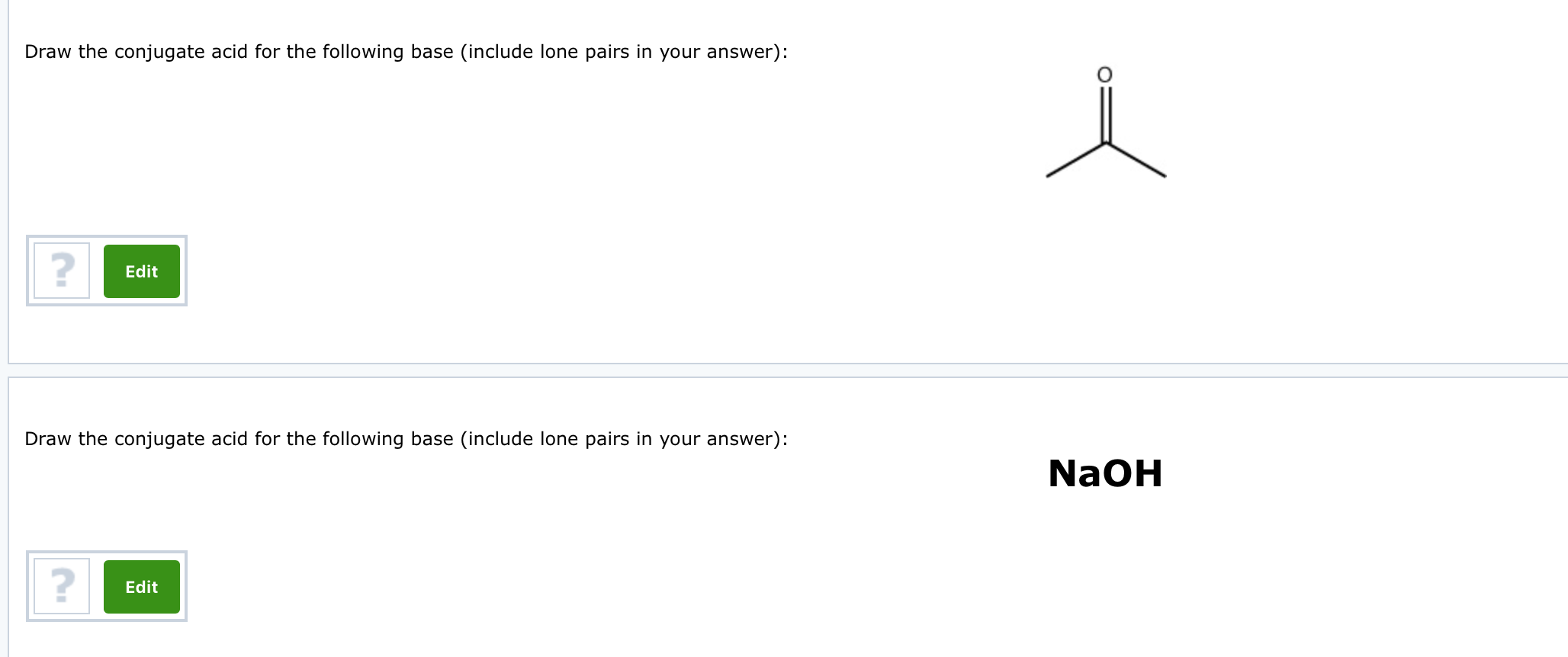
Solved Draw the conjugate acid for the following base
The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming.
How To Draw A Conjugate Acid
For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺.
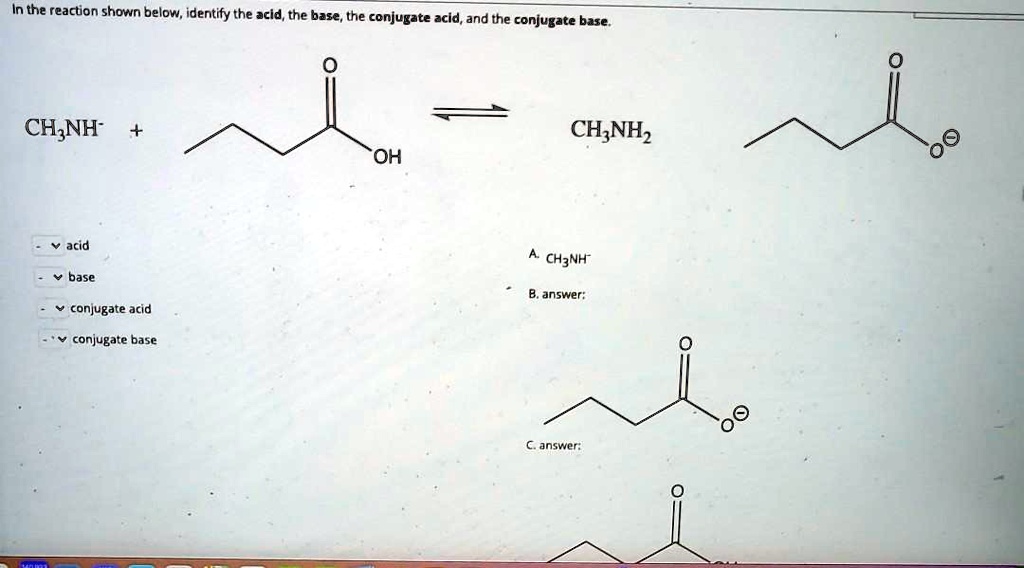
SOLVED In the reaction shown below, identify the acid; the base, the
Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction:
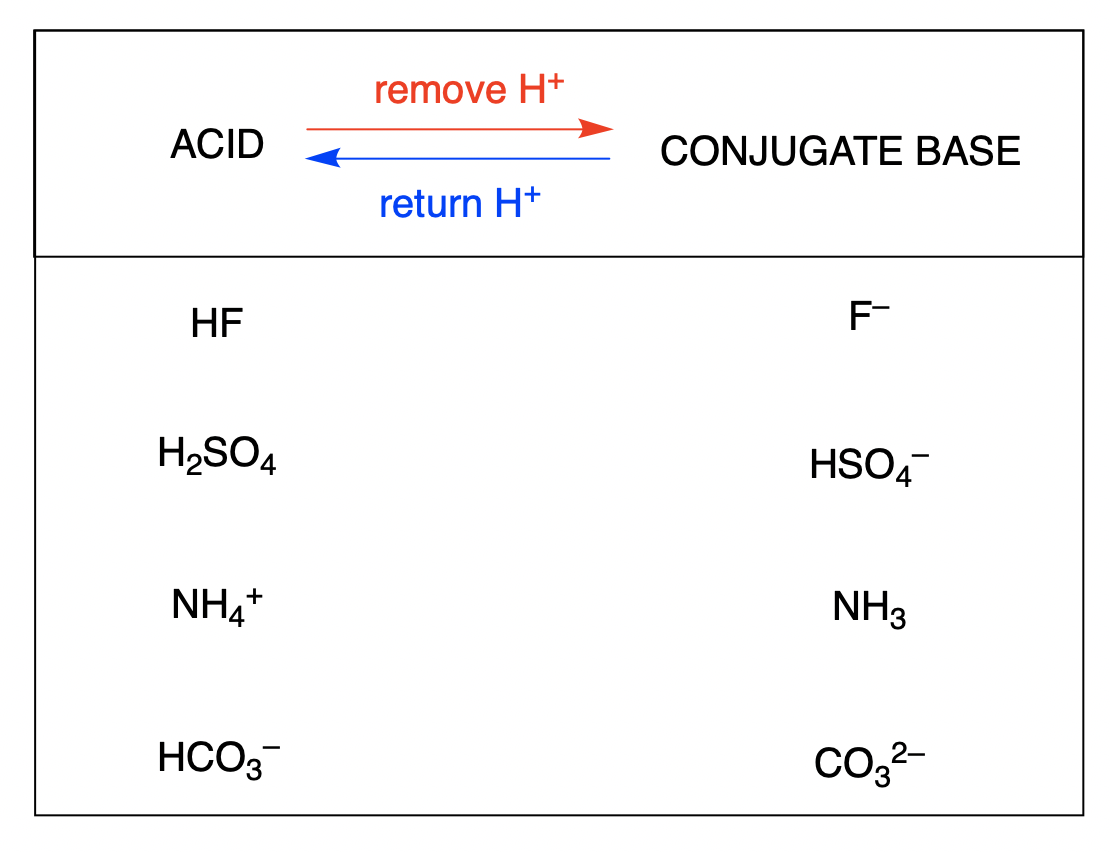
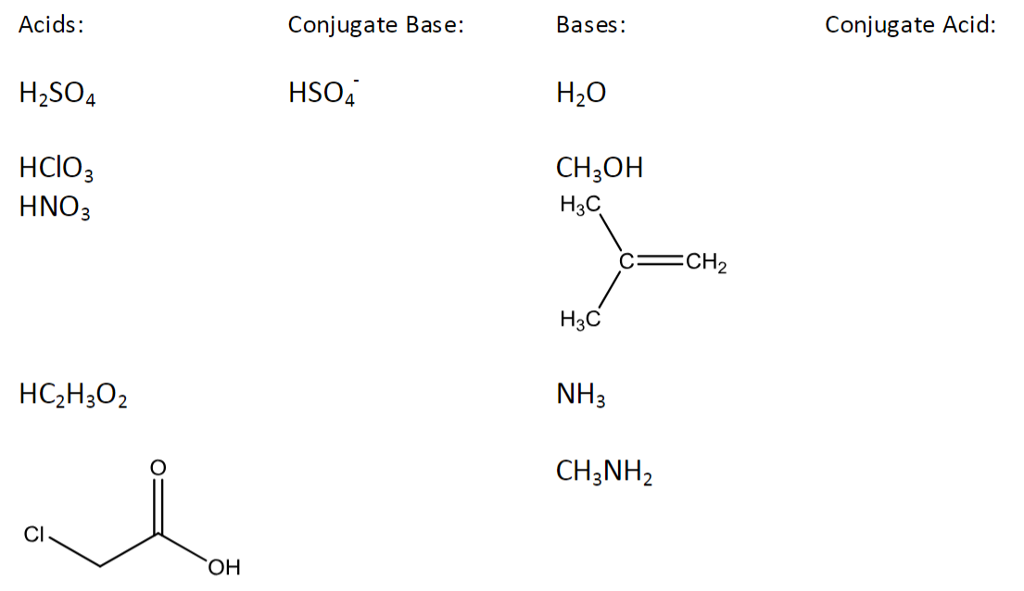
Solved Bases Conjugate Acid Conjugate Base Acids H2SO4
The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+.
Solved Identify the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate
Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming.
Solved What Is The Conjugate Acid Of HSO4? What Is Conju...
For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. The formula for the conjugate acid of ch₃nh₂ (methylamine) is ch₃nh₃⁺. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming.
The Formula For The Conjugate Acid Of Ch₃Nh₂ (Methylamine) Is Ch₃Nh₃⁺.
Therefore, the conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. When ch₃nh₂ acts as a base, it accepts a proton (h⁺), forming. The conjugate acid of ch3nh2 is ch3nh3+. For example methylamine in water chemical reaction: