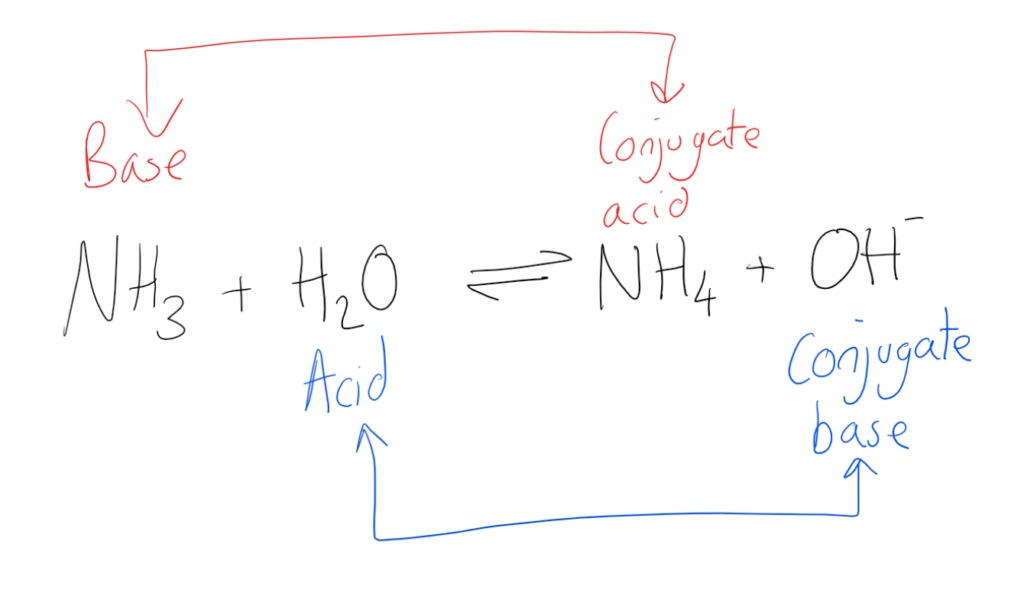
What Is The Conjugate Base Of Hco3 - When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. For each case give the corresponding.
For each case give the corresponding. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its.
For each case give the corresponding. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Solved Give The Conjugate Base For Each Compound Below. A...
Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. For each case give the corresponding. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its.
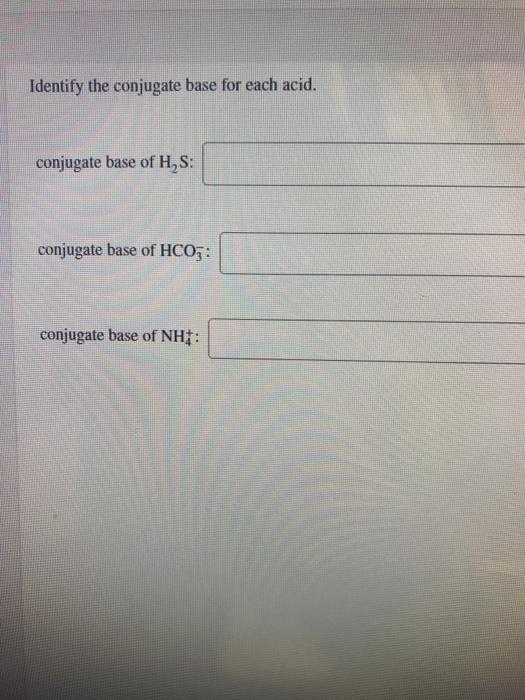
Solved Identify the conjugate base for each acid. conjugate
Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. For each case give the corresponding. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Conjugate acid and conjugate base of HCO3− respectively are Filo
For each case give the corresponding. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Conjugate Acids And Bases Acid Base Equilibria
Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. For each case give the corresponding. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its.
Conjugate Base Of H3po4 Asking List
For each case give the corresponding. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Solved Identify the conjugate base for each acid. conjugate
When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. For each case give the corresponding. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Conjugate AcidBase Pairs — Overview & Examples Expii
When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. For each case give the corresponding. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because.
SOLVED What is the conjugate base for HCH3CO2 and the conjugate base
For each case give the corresponding. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because.
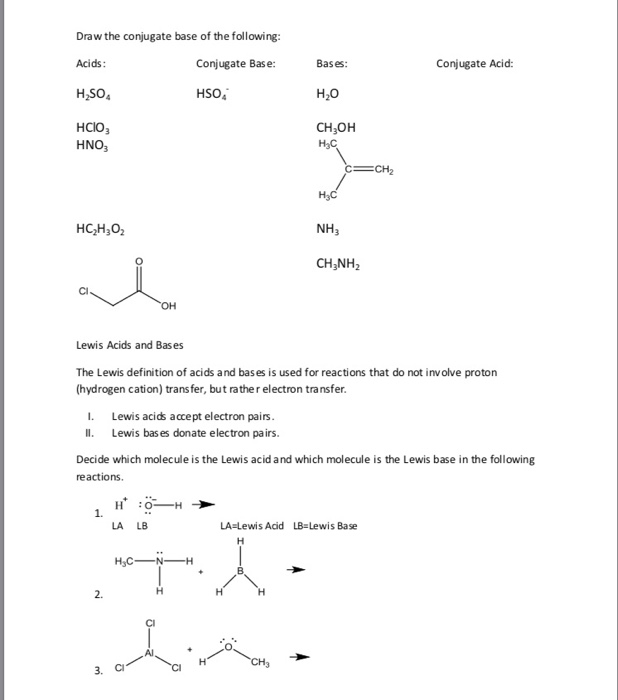
Solved Draw the conjugate base of the following Acids
Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. For each case give the corresponding. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its.
Solved The conjugate base of H2CO3 is H2CO3 HCO3 CO32 O
Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its. For each case give the corresponding. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons.
Conjugate Acids And Conjugate Bases Are The Acids And Bases That Lose Or Gain Protons.
For each case give the corresponding. Nh4+ is the conjugate acid to the base nh3, because. When an acid, like bicarbonate ion, donates a proton, it transforms into its.