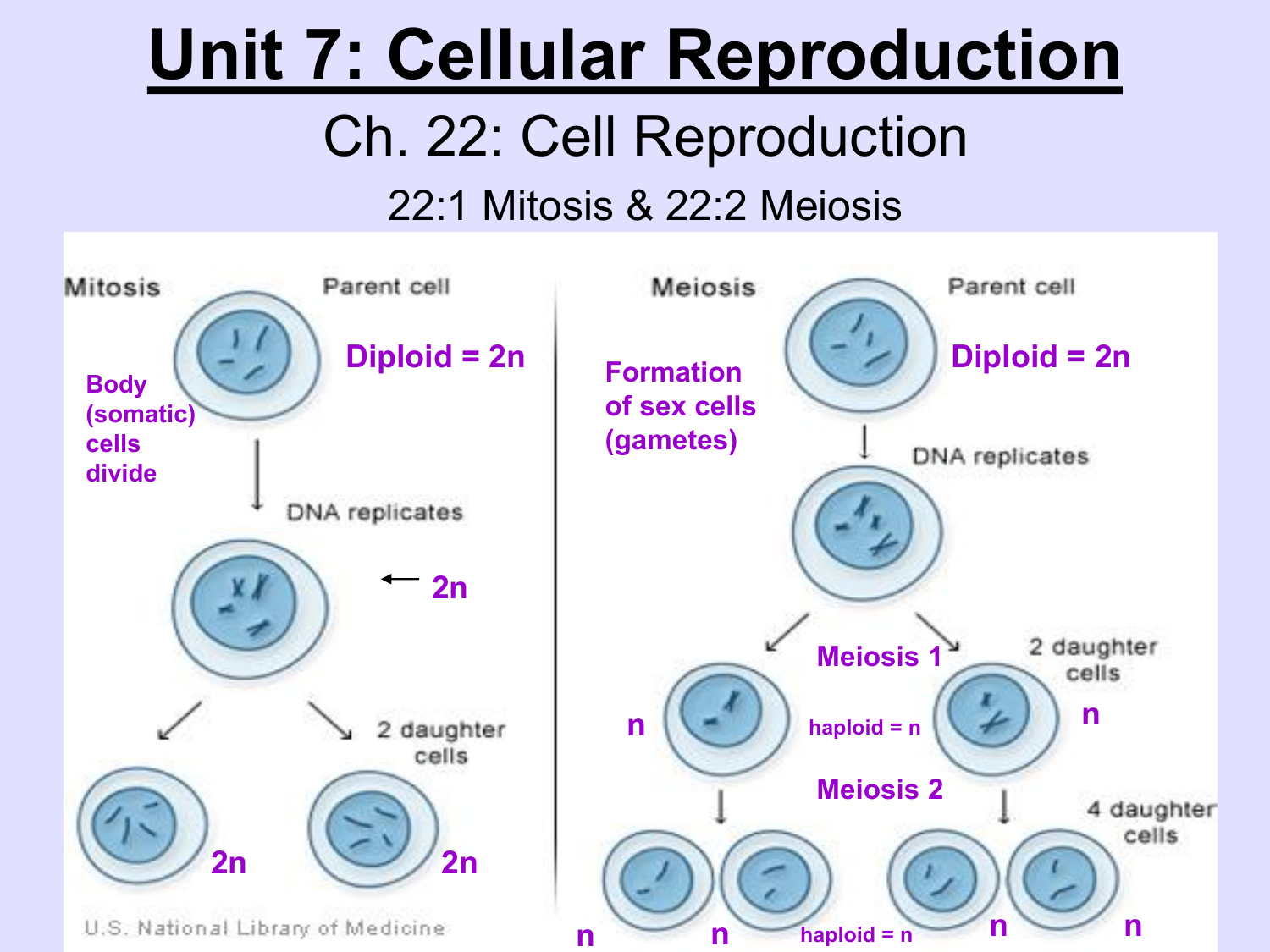
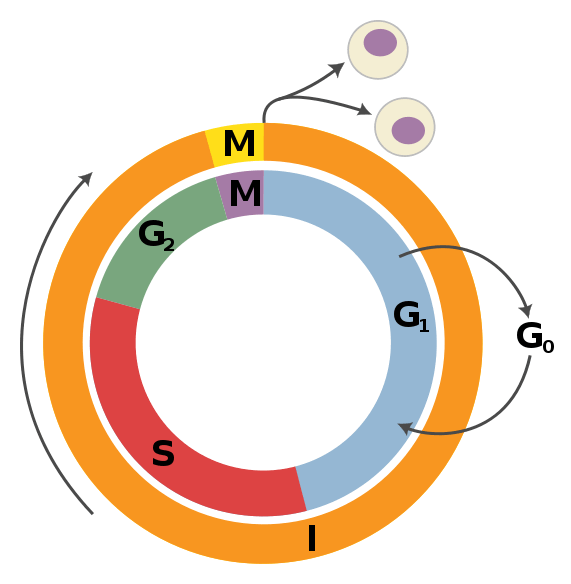
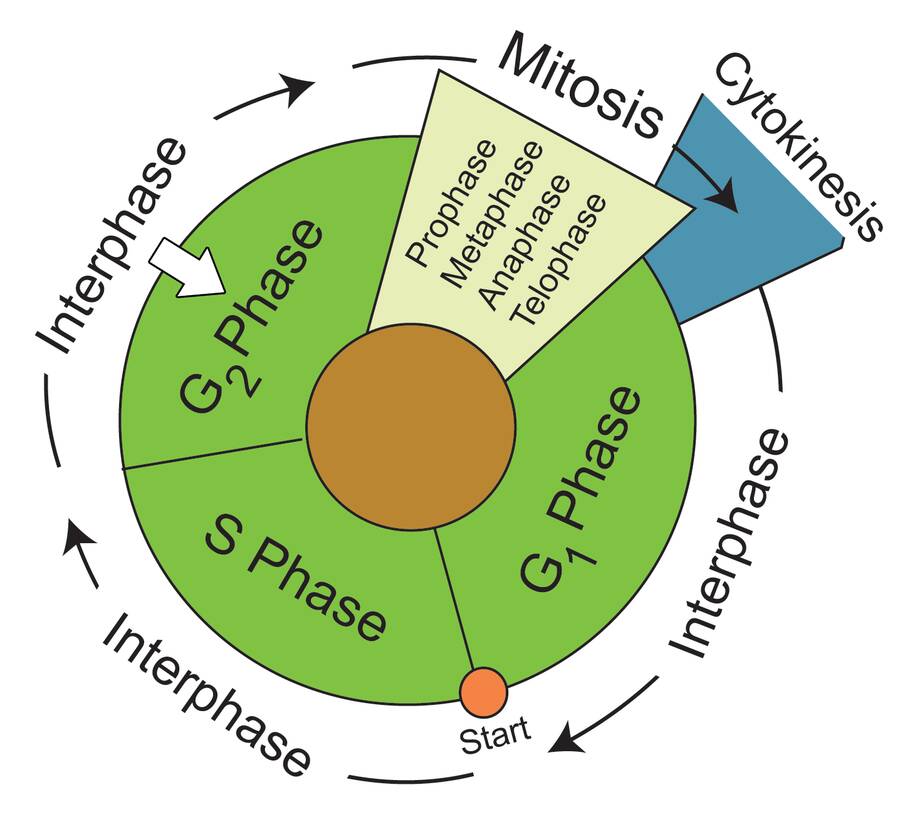
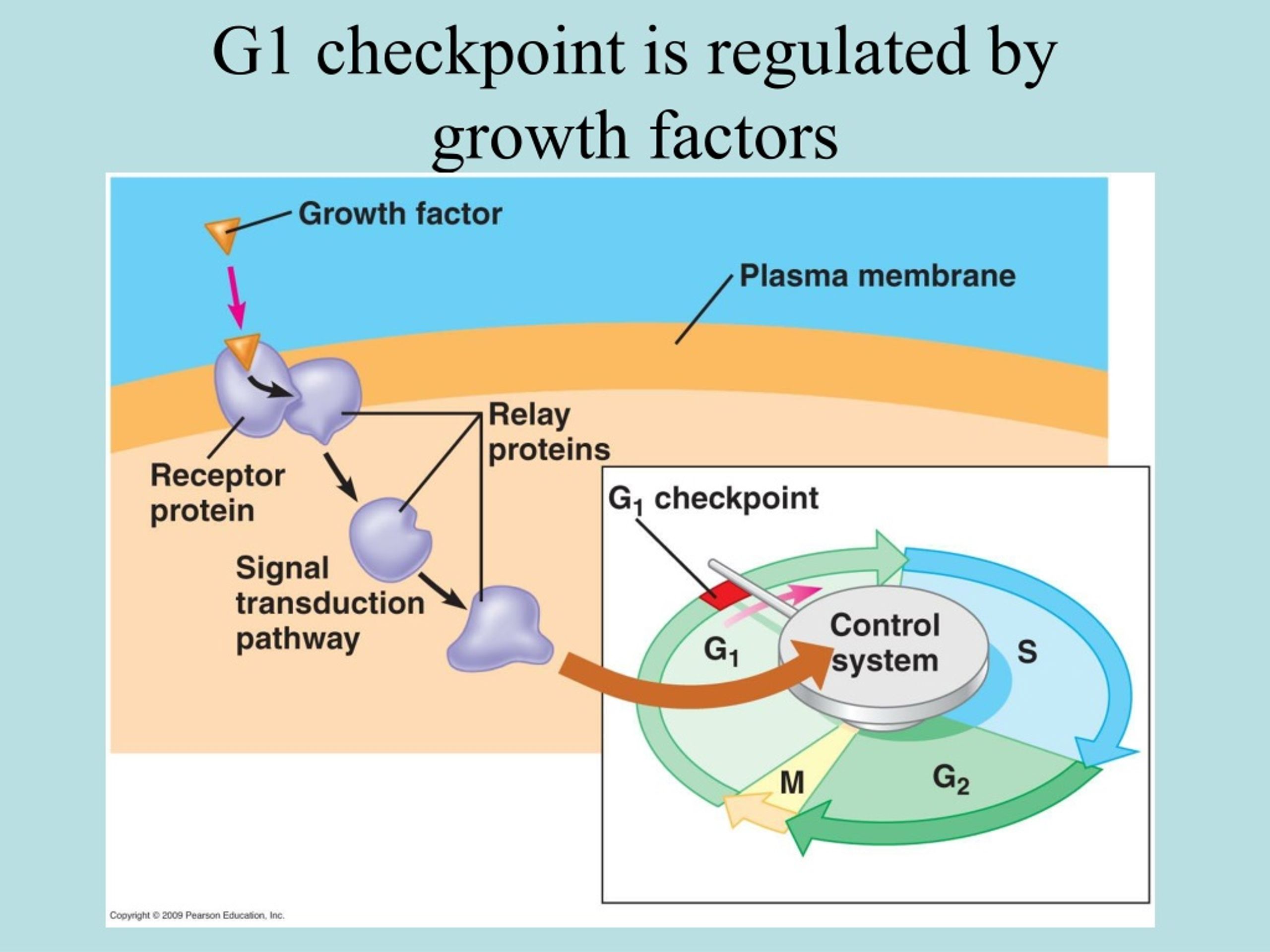
What S Evaluated At The G2 Checkpoint In Mitosis And Meiosis - Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed to proceed to. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2.
Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed to proceed to. Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? Begins in late s phase and continues through g2.
For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed to proceed to. Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2. The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged.
Types Of Mitosis
Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed to proceed to. Because cyclin is protected from degradation.
Mitosis vs Meiosis
For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? The g2 checkpoint.
Cellular Division Mitosis and Meiosis (Video & Fact Sheet)
For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2..
Cell Biology, Mitosis Cell Cycle
Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2. The g2/m.
Mitosis Introduction to Biology The Cell Cycle
The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. For example, because a cell with damaged dna can lead to cancer if it is allowed. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters..
PPT & Medicine 1. The Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Cancer
The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed to proceed to. Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna.
G1 Checkpoint Monitors Cell Size and Integrity G2 Checkpoint DNA
The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is.
Mitosis vs Meiosis
Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint? The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2. The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed.
Bio 100 checkpoint mitosis and meiosis by supermoon10 Issuu
Begins in late s phase and continues through g2. Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter.
Mitosis Mitosis through Meiosis
The g2/m checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining genomic stability by ensuring that any dna damage is repaired before a cell enters. The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the.
For Example, Because A Cell With Damaged Dna Can Lead To Cancer If It Is Allowed.
Because cyclin is protected from degradation during late s phase and g2. The g2 checkpoint ensures all of the chromosomes are replicated and that the replicated dna is not damaged before the cell. The g2 checkpoint is a crucial stage in the cell cycle where several key evaluations take place before a cell is allowed to proceed to. Begins in late s phase and continues through g2.
The G2/M Checkpoint Plays A Vital Role In Maintaining Genomic Stability By Ensuring That Any Dna Damage Is Repaired Before A Cell Enters.
The g2 checkpoint assesses the completeness of dna replication, ensuring that the cell does not enter mitosis with unreplicated or damaged. Which condition is evaluated at the g2/m checkpoint?