When Substrate Level Phosphorylation Occurs It Means That - When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. B) nadh is converted into nad + h. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. C) nad is converted into nadh.
D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. C) nad is converted into nadh. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. B) nadh is converted into nad + h.
D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. C) nad is converted into nadh. B) nadh is converted into nad + h.
When Substrate Level Phosphorylation Occurs It Means That
Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? C) nad is converted into nadh. B) nadh is converted into nad + h. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops.
When Substrate Level Phosphorylation Occurs It Means That
Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. B) nadh is converted into nad + h.
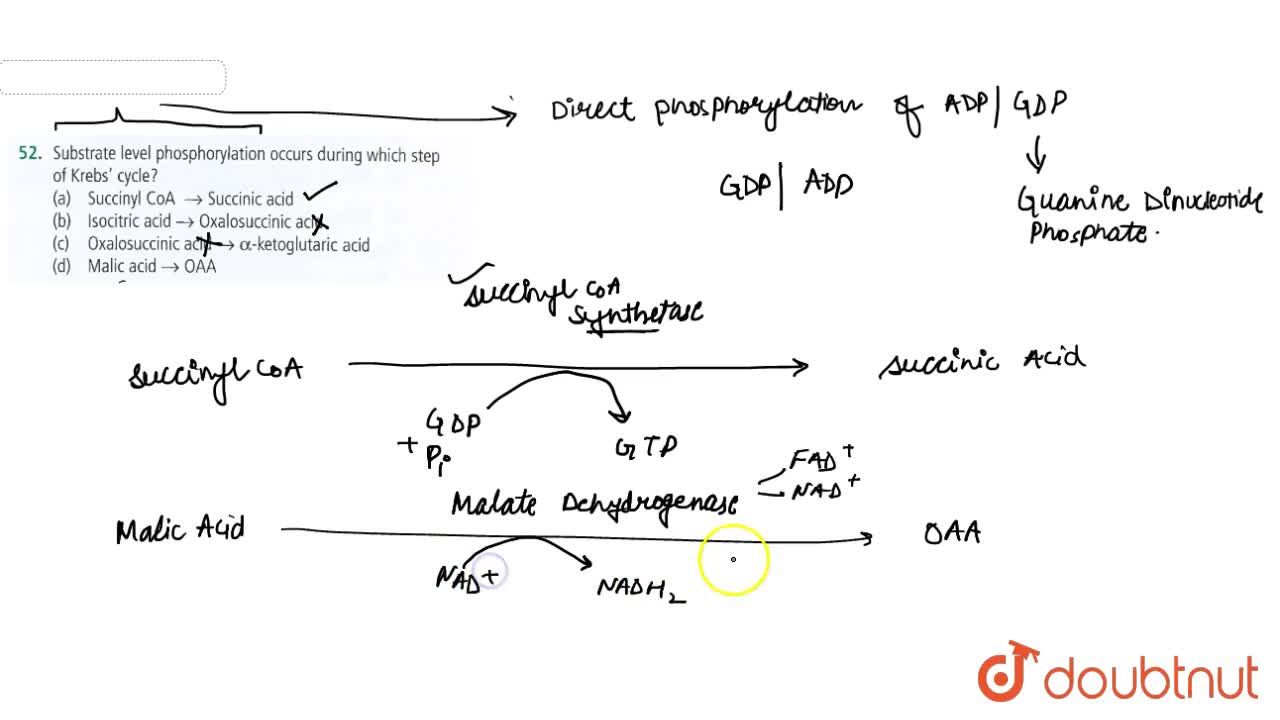
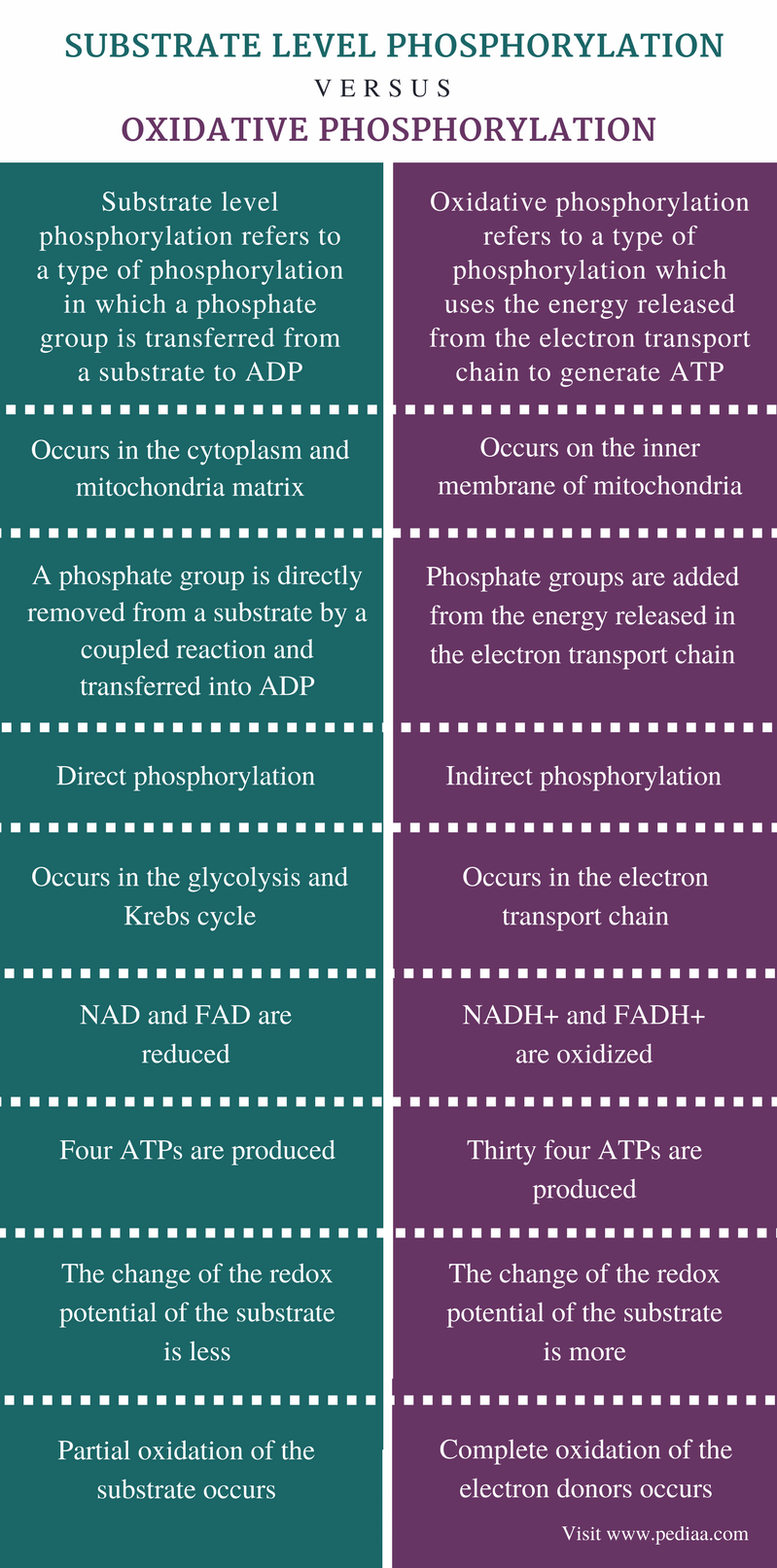
Compare and contrast substratelevel phosphorylation and oxidativ
Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. C) nad is converted into nadh. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell?
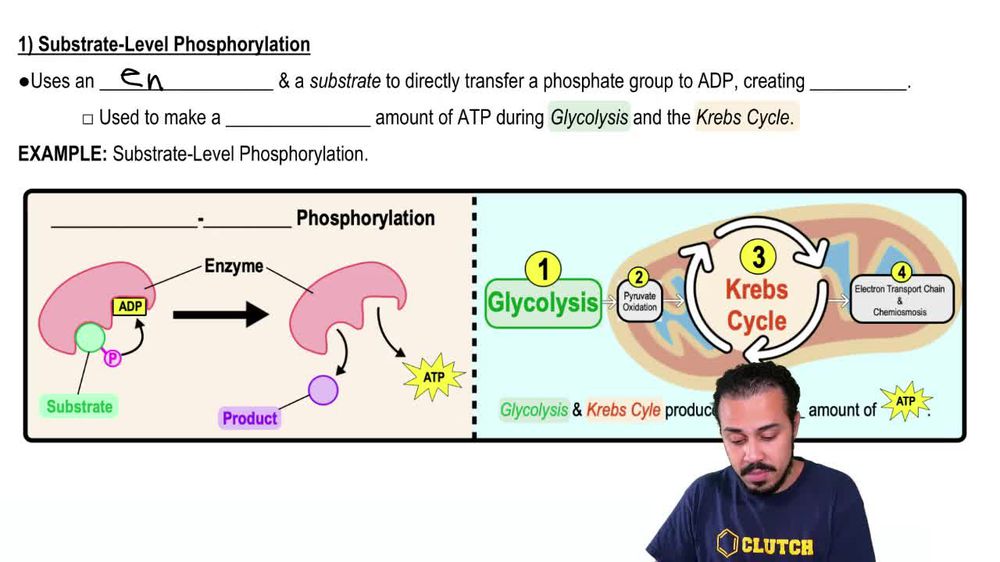
Solved Substrate level phosphorylation Occurs as a result
D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? C) nad is converted into nadh. B) nadh is converted into nad + h. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops.
Solved Substrate level phosphorylationuse P attached to
When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. C) nad is converted into nadh.
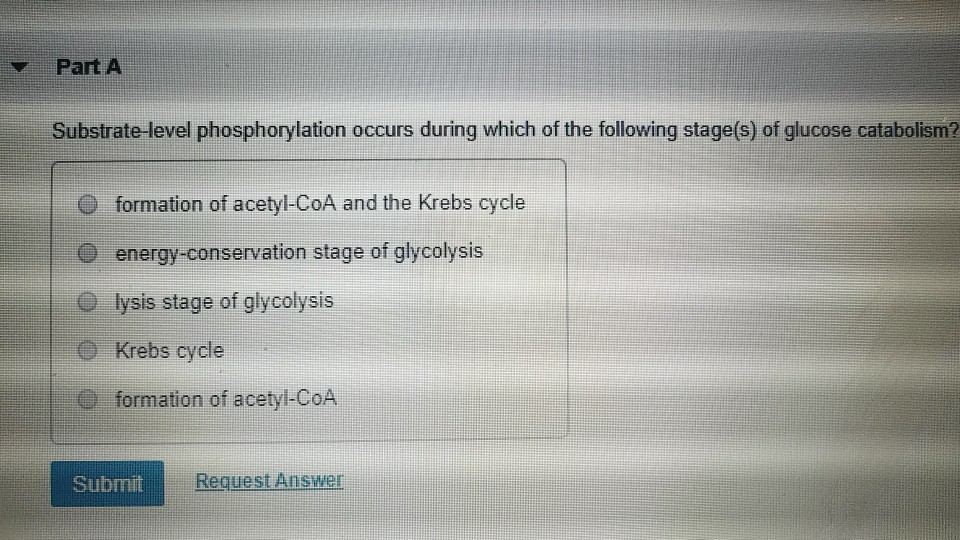
Solved Part A Substratelevel phosphorylation occurs during
B) nadh is converted into nad + h. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. C) nad is converted into nadh. D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group.
Solved Substratelevel phosphorylation occurs in
D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? C) nad is converted into nadh. B) nadh is converted into nad + h.
Solved Substratelevel phosphorylation occurs. a. In
Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. B) nadh is converted into nad + h. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. C) nad is converted into nadh.
Solved Substratelevel phosphorylation occurs in Multiple
Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. B) nadh is converted into nad + h. When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____.
Substratelevel Phosphorylation Definition, Example, & Importance
When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell? C) nad is converted into nadh. Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____.
B) Nadh Is Converted Into Nad + H.
Once a critical temperature is reached, the reaction stops. Being an exergonic reaction, it releases some free. D) amp is converted into nad by adding a phosphate group. Why does this happen?, enzymes lower _____.
C) Nad Is Converted Into Nadh.
When cells possess plentiful amounts of atp, what happens to cellular respiration processes within the cell?